Fig. 4.
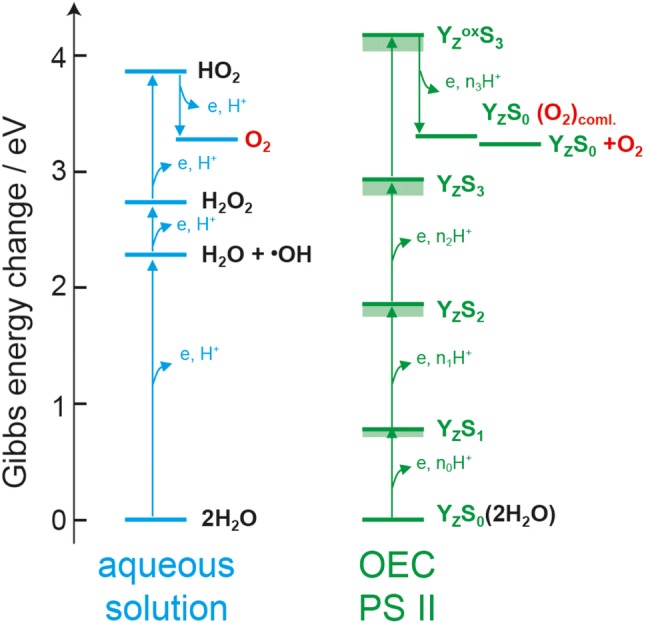
Gibbs energy (in eV) required to oxidize water stepwise in aqueous solution (left) and in the OEC of PS II (right). In particular the removal of the first electron from water (left) requires much energy (> 2 eV) that cannot be provided in a biological system. Thus, in the OEC, water is not oxidized by subsequent single electron removal from substrate water. Instead, it is the Mn cluster that is oxidized by four successive oxidation events; the two attached substrate water molecules release the protons (for charge neutrality), and O2 is released only in the last step after O–O bond formation in a concerted reaction. Thereby, high-energy steps are avoided and the redox process is leveled. Figure adapted from (Messinger and Renger 2008)
