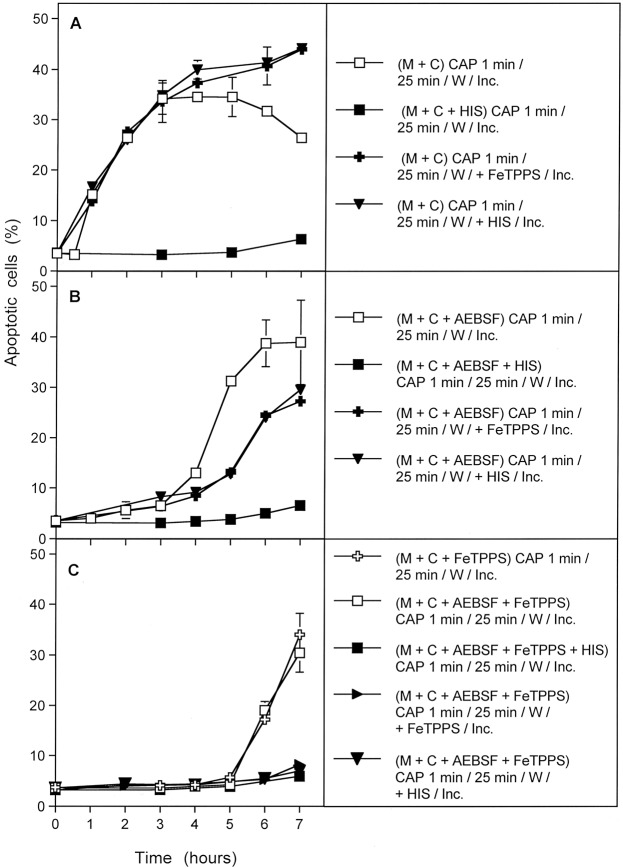
Figure 11.
The kinetically determined, CAP-induced processes show differential response to early and late addition of inhibitors. The experiments were performed in analogy to those described in Fig. 10. In addition, parallel assays also received either 2 mM of the singlet oxygen (1O2) scavenger histidine or 25 µM of the peroxynitrite (ONOO−) decomposition catalyst FeTPPS after the washing step that followed CAP treatment and the first incubation step of 25 min. Assays without CAP treatment showed less than 5% apoptotic cells at all time points (not shown in the graph). (A) Process #1 was inhibited when histidine was present during CAP treatment and the first 25 min incubation step, but not when histidine had been added after the washing step. Likewise, FeTPPS added after the washing step had no inhibitory effect. (Note that addition of FeTPPS during CAP treatment would have shifted process #1 to process #3, shown below). Process #1 is the overall process, based on unlimited primary and secondary singlet oxygen generation. (B) Process #2 was induced when AEBSF was present during CAP treatment and the 25 min incubation step. Process #2 was completely inhibited by the presence of histidine during CAP treatment and the 25 min incubation step, and partially inhibited when histidine or FeTPPS had been added after the washing step. Process #2 reflects the regime in which secondary 1O2 generation is blocked during CAP treatment and the subsequent 25 min incubation step. After the washing step, secondary 1O2 generation resumes, driven by the imprinted signature established initially by primary 1O2generated by long-lived species of CAP-treated medium. (C) Process #3 is independent of ONOO− and NOX derived O2●− during CAP treatment and the 25 min incubation step, but completely dependent on 1O2 at this step. The process after the washing step is completely dependent on 1O2 and on ONOO−. Process #3 depends on the imprinted signature by primary 1O2 from the gaseous phase of CAP. The imprinted signature drives secondary 1O2 generation after the washing step.