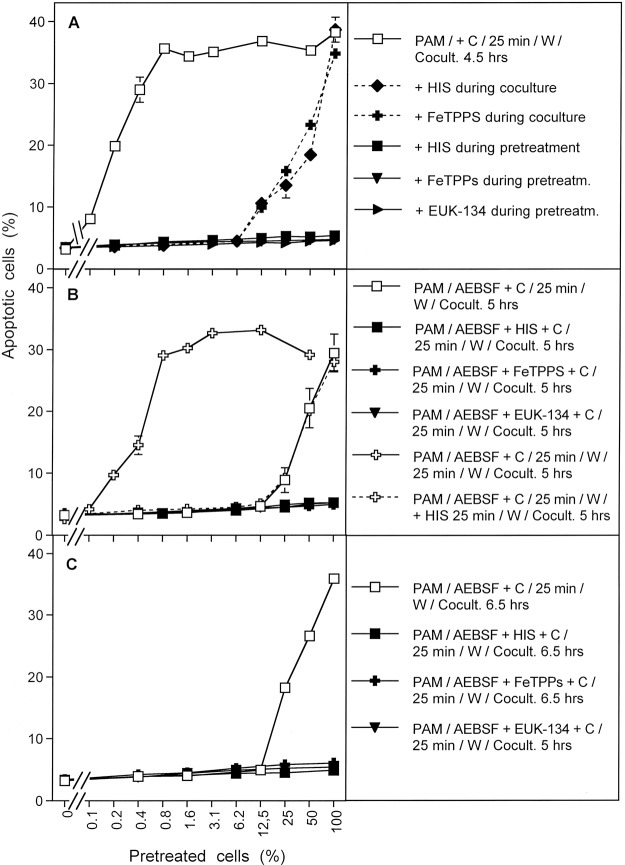
Figure 15.
Bystander effect-inducing potential after treatment of tumor cells with PAM. (A) Medium was treated with CAP for 1 min. The resultant PAM was added to cells and the mixture was incubated for 25 min. After a washing step of three cycles, increasing percentages of pretreated cells were added to untreated cells and the percentages of apoptotic cells were determined after 4.5 h. Parallel assays were performed analogously, with the modification that histidine (“HIS”, 2mM) or FeTPPS (25 µM) or EUK-134 (25 µM) were either present during pretreatment of cells with CAP, or during the coculture between pretreated and untreated cells. (B) PAM was mixed with tumor cells and AEBSF was added to all assays. Then the assays received either no further addition, or addition of 2 mM histidine, 25 µM FeTPPS or 25 µM EUK-134. All assays were incubated for 25 min and then washed. Increasing concentrations of pretreated cells were added to untreated cells and the percentages of apoptotic cells were determined after 5 h In additional assays, coculture of PAM and cells in the presence of AEBSF was performed for 25 minutes. Then the cells were washed, resuspended in fresh medium and incubated for 25 min in the absence of inhibitors (open cross) or in the presence of histidine (open cross, dashed line). Then the cells were washed again and added to untreated cells at increasing concentrations. Apoptosis induction was determined after 5 h. (C) The assays defined by open squares, closed squares, closed crosses and closed triangles under B were cultivated for 6.5 h and then apoptosis induction was determined. These data show that PAM induces strong bystander inducing potential, provided the generation of primary and secondary 1O2 is not prevented. Prevention of secondary 1O2 caused a dramatic loss of bystander inducing cells. A high potential can, however, be recovered, when AEBSF is removed from the cells and an incubation step of 25 min is allowed in fresh medium. The recovery of the inducing potential is mediated by 1O2.