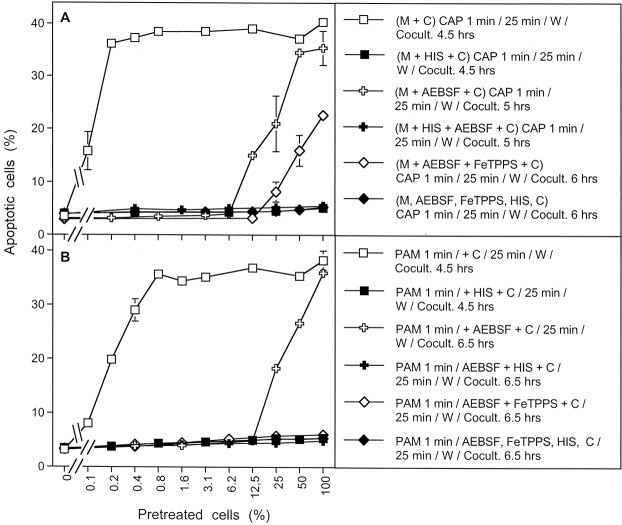
Figure 16.
Induction of bystander effects by CAP and PAM. (A) MKN-45 cells were treated with CAP for 1 min, followed by an incubation step of 25 min in the same medium. After a washing step of three cycles, increasing percentages of pretreated cells were added to untreated tumor cells (open squares). The percentages of apoptotic cells in these cocultures were determined at the indicated times. This basis approach was modified by either adding the NOX1 inhibitor AEBSF (100 µM) during CAP treatment and initial incubation (open crosses), and in this way blocking the generation of secondary 1O2, or adding AEBSF and the ONOO− decomposition catalyst FeTPPS (25 µM) (open diamonds), and in this way allowing to focus on 1O2 derived directly from the gaseous phase of CAP, as the generation of 1O2 from long-lived species in the medium and secondary 1O2 generation by the cells was prevented under these specific conditions. All modifications were studied in parallel in the presence of histidine during pretreatment (closed symbols) to allow the evaluation of the role of 1O2. (B) The experiment was performed in an analogous mode to A, with the exception that the cells were not treated with CAP in medium, but were mixed (50%) with PAM that had been prepared by treating medium with CAP for 1 min. The results show that maximal bystander inducing potential is achieved when CAP or PAM treatment is applied without experimental interference with primary or secondary 1O2 generation (open squares). Prevention of secondary 1O2 generation causes a dramatic loss of bystander effect-inducing cells both after CAP and PAM treatment (open crosses). This effect is essentially due to primary 1O2 generated by long-lived species (i. e. H2O2 and NO2−). Direct treatment of cells in medium in the presence of AEBSF and FeTPPS (Fig. 11A) allows to detect the effect of 1O2 derived from the gaseous phase of CAP (open diamonds) which is lower than the effect by 1O2 generated by long-lived species (open crosses). In assays treated with the PAM regime (Fig. 11B), no effects due to 1O2 derived from the gaseous phase of CAP were detected, consistent with the short life time of 1O2.