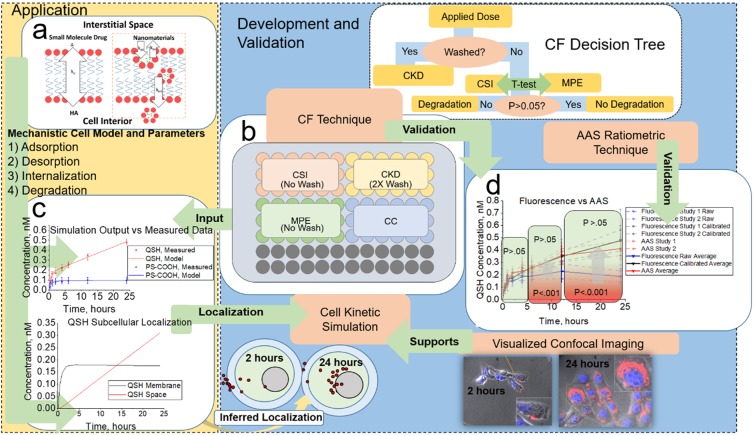
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of FORECAST. The CF assay is coupled to an in vitro kinetics simulation. (a) Traditional partition coefficients (kp) commonly used for small molecule partitioning between blood supply and cell interior. For NMs, rate constants for adsorption (kad), desorption (kde), internalization (kint), and degradation (kdeg) more accurately represent uptake processes incident on a NM when exposed to cell environment. (b) Layout of CF assay, including CSI compartment (internal standard and descriptive of cellular degradation), CKD compartment (descriptive of kinetics of NM-cell interactions), MPE compartment, (descriptive of media degradation), and CC compartment (descriptive of control with cells without NM exposure). The CF decision tree illustrates how these are connected in the assay. CF outputs were then used to build a simulation (c) with parameters descriptive of adsorption, desorption, internalization, and degradation pathways. Data from CF was also (d) validated to AAS outputs.