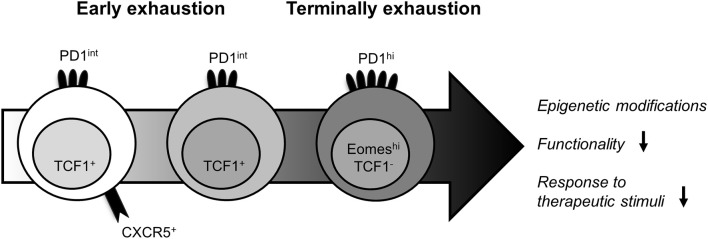
Figure 1.
Heterogeneity of exhausted LCMV-specific CD8+ T cells. The identification of functionally distinct T-cell subpopulations within exhausted LCMV-specific CD8+ T cells has enabled the definition of their lineage dynamics. Despite the epigenetic fingerprint of T-cell exhaustion, the expression patterns of several phenotypical and transcriptional markers can discriminate between less exhausted and terminally exhausted LCMV-specific CD8+ T cells. While the early differentiated LCMV-specific CD8+ T-cell subpopulation is defined by co-expression of PD1, CXCR5, and TCF1 and provides a strong response to therapeutic stimuli, the more differentiated PD1int TCF1+ LCMV-specific CD8+ T-cell subpopulation still harbors some effector function. In contrast, the terminally exhausted PD1hi, Eomeshi LCMV-specific CD8+ T-cell population exhibit a more severely impaired functionality and is unresponsiveness to immunotherapies.