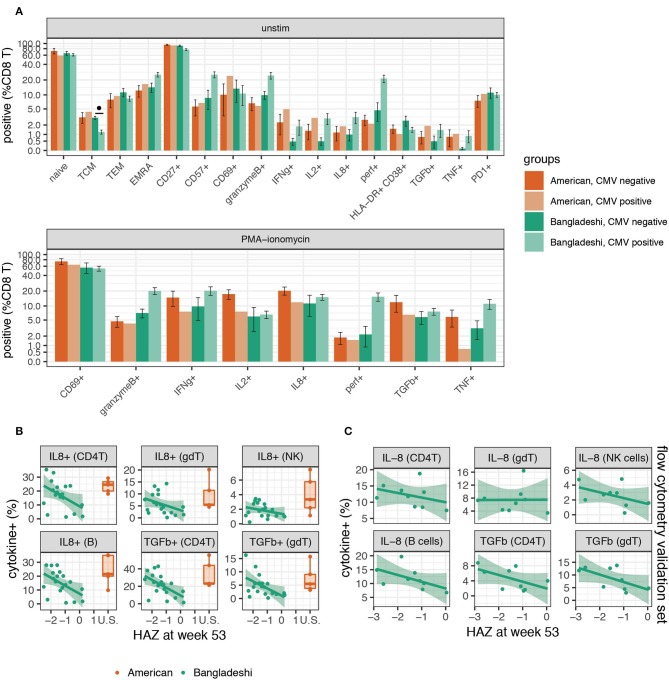
Figure 6.
Higher functional responses to stimulation are associated with stunting in Bangladeshi 1-year-olds. (A) Frequencies of CD8 T cells with and without stimulation in CMV positive and negative 1-year-olds. Mann-Whitney tests were performed for each population shown. p-values were then corrected for multiple testing using the Benjamini and Hochberg method. Significant differences in cell population frequencies between Bangladeshi CMV positive and negative subjects are indicated by FDR < 0.1 (•). Values plotted are means ± SEM. The number of donors in each group were n = 4 and 14 Bangladeshi CMV negative and positive, respectively, in unstimulated samples; n = 3 and 16 Bangladeshi CMV negative and positive, respectively, in stimulated samples; n = 4 American CMV negative for unstimulated and stimulated samples; n = 1 CMV positive American child for unstimulated and stimulated samples. (B) Relationship between stunting (as measured by height for age z-score, HAZ) and IL-8 or TGFβ cytokine production in unstimulated or PMA-ionomycin stimulated PBMCs from Bangladeshi 1-year-olds (n = 8 less stunted; n = 8 more stunted). After permuting HAZ scores 5,000 times and setting a cut-off of p = 0.05 and FDR = 0.2, we identified IL-8 and TGFβ in stimulated PBMCs as significantly associated with HAZ across multiple populations. No significance was found in unstimulated populations. After PCA and a validation (C) set analysis (n = 9), the combined p-values from training and validation sets were p = 0.009 (IL-8) and p = 0.002 (TGFβ) using the first principal component. Values from American children (n = 5) are presented for comparison purposes.