Figure 7.
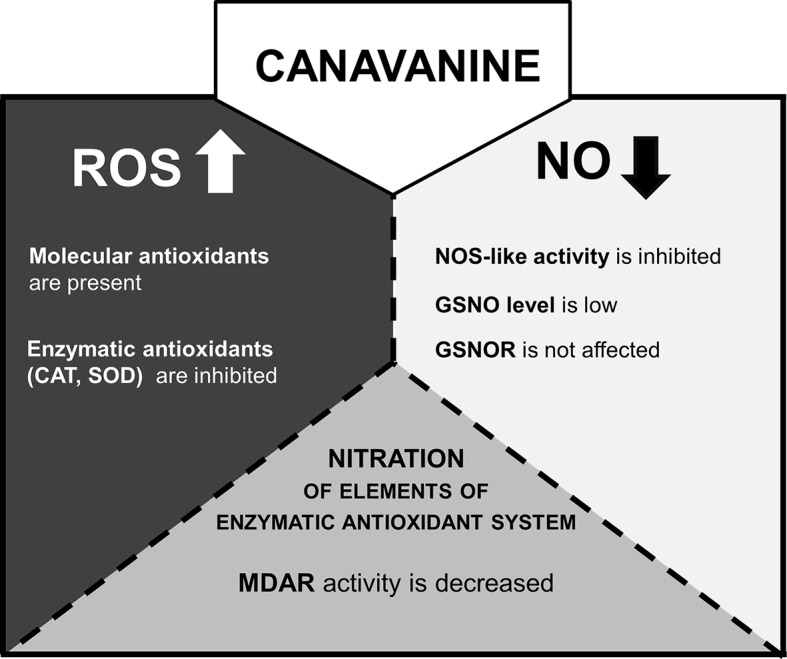
The model of CAN action in tomato roots after prolonged (72 h) supplementation of seedlings with the NPAA. CAN increases level of ROS (Krasuska et al., 2016a) and decreases NO emission (Krasuska et al., 2016a). ROS are accumulated (CAN secondary mode of action) and could inhibit GSNOR activity by oxidative PTMs (Lindermayr, 2018). However, the gene expression and activity of GSNOR are not affected. GSNO level is lowered probably due to limitation of NO resulting from restriction of NOS-like activity (direct mode of action of CAN). ROS over-accumulation is accompanied by stimulation of molecular antioxidant system. CAT or SOD gene expression is downregulated, CAT and SOD enzymatic activities are inhibited. MDAR is an enzymatic antioxidant and the target of differential nitration in CAN-supplemented plants.
