FIGURE 5.
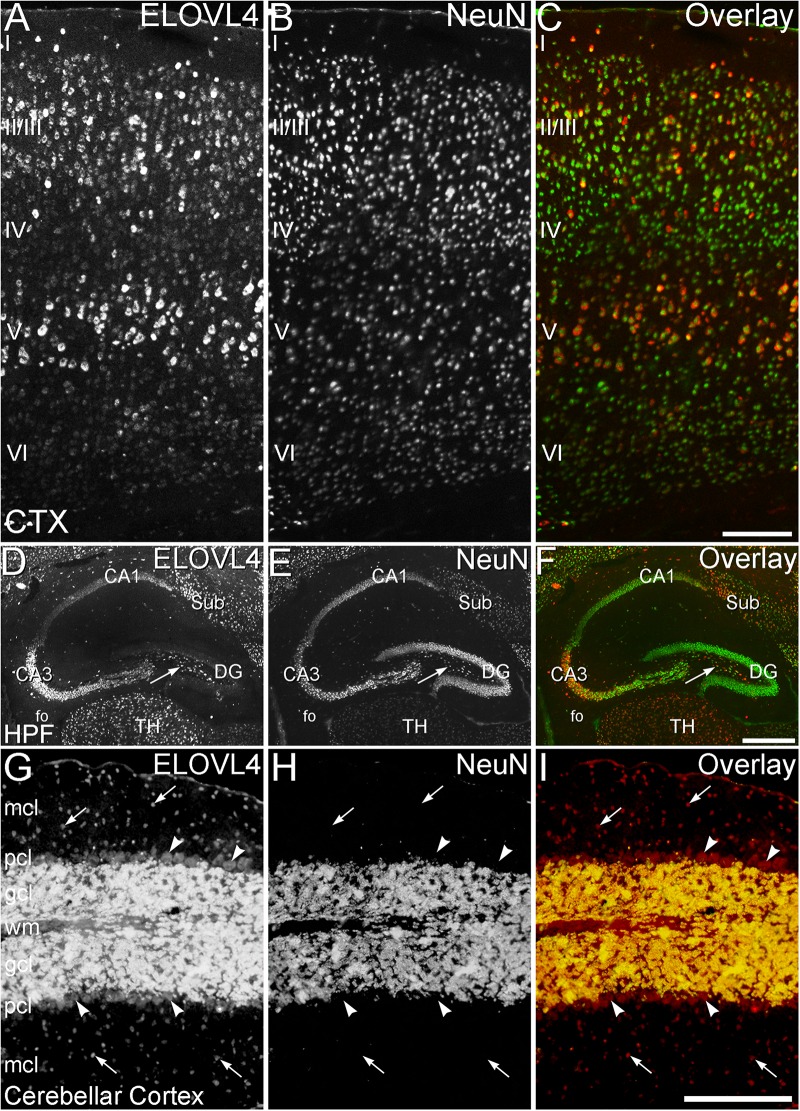
Cell-specific expression of ELOVL4 in isocortex, hippocampus and cerebellum. (A–C) Cerebral Cortex (CTX). (A) Labeling for ELOVL4 is present in all layers of the cerebral cortex (CTX). Cells in the pyramidal layers (II/III and V) are most prominently labeled, but ELOVL4-positive cells also are present in the molecular layer (I), layer 4 (IV) and layer 6 (VI). (B) Labeling for the neuronal marker, NeuN. (C) Overlay of panels A and B shows close correspondence of ELOVL4 (red) and NeuN labeling (green). (D–F) Hippocampal formation (HPF). (D) Labeling for ELOVL4 is present in the cellular layers of the HPF, including the Cornu Ammonis, with field 1 (CA1) showing less prominent labeling than field 3 (CA3). Prominent ELOVL4 labeling also is present in the subiculum (sub) and interneurons in the polymorph layer (arrow). Cells along the inner margin of the dentate gyrus (DG) show moderate ELOVL4 labeling, but most dentate granule cells show little ELOVL4 labeling. (E) Labeling for the neuronal marker, NeuN. (F). Overlay of (D,E) shows close correspondence of ELOVL4 (red) and NeuN (green) labeling. TH, Thalamus. (G–I) Cerebellar cortex. (G) Cross section through a cerebellar folium showing ELOVL4 expression in the cerebellar cortex. Neurons (arrows) in the molecular cell layer (mcl) show strong ELOVL4 labeling, but the Purkinje cells (arrowheads) in the Purkinje cell layer (pcl) show only moderate levels of ELOVL4 labeling. The densely packed cells of the granule cell layer (gcl) show very intense labeling. (H) Labeling for the neuronal marker, NeuN, strongly labels neurons in the gcl, but not Purkinje cells, as appropriate. (I) Overlay of (G,H) shows close correspondence of intense ELOVL4 (red) and NeuN (green) labeling resulting in an orange color in the gcl. wm, white matter of the arbor vitae. Scale bars = 200 μm for (A–C,G–I); 500 μm for (D–F) (figure from Sherry et al., 2017; used with open access under the Creative Commons attribution license CC-BY, version 4.0; http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).