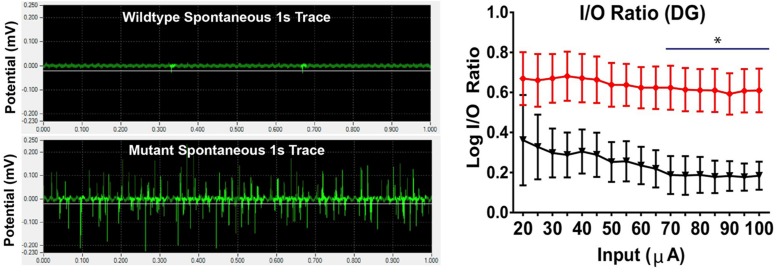
FIGURE 8.
Seizure activity resulting from STGD3 deletion. Left: Spontaneous bursting activity in hippocampal slices from S+Elovl4mut/mut mice with knock-in of the 5 bp STGD3 mutation and skin-specific rescue of wildtype (WT) ELOVL4 function to prevent perinatal lethality, and S+Elovl4wt/wt control mice expressing the WT ELOVL4 gene under baseline conditions. Representative traces of field potentials from postnatal day 19 S+Elovl4wt/wt (upper trace) and S+Elovl4mut/mut mice (lower trace). Each trace represents the first 1 s of a single channel chosen from a 10 min recording taken using a 64 channel multi-electrode array. The S+Elovl4mut/mut slice shows a dramatic increase in spontaneous neuronal activity compared to WT littermates. Right: Stepwise increased stimulations to perforant path synapses in dentate gyrus (DG) revealed a markedly enhanced input/output (I/O) ratio indicating a boost in synaptic strength in the main input pathway from the entorhinal cortex of S+Elovl4mut/mut mice (red) compared to S+Elovl4wt/wt control mice (statistics: two-way RM ANOVA, ∗p < 0.05 from 70 to 100 μA). Reproduced from Hopiavuori et al. (2018) with the permission under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (link to the Creative Commons license; http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).