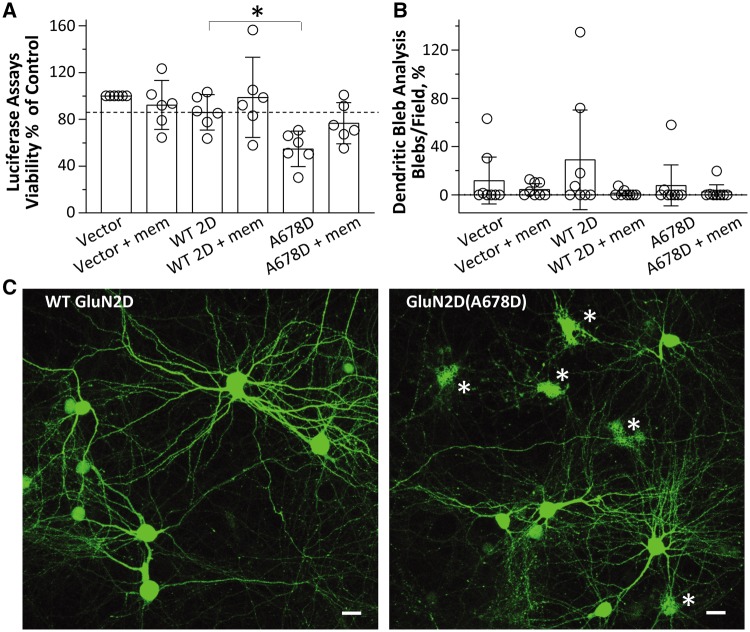
Figure 5.
The GluN2D-A678D variant induces neurotoxicity. Transfection of GluN2D(Ala678Asp) into cultured cortical neurons reduces cell viability, which can be prevented by the low affinity NMDAR antagonist memantine. (A) The mean cell viability determined by a Luciferase assay is shown as a per cent of control group (Vector) (% control) with wild-type GluN2D (–), 83%; wild-type GluN2D, 86%; GluN2D-A678D, 55%; GluN2D-A678D + mem, 77%. mem = 50 μM memantine; *P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (bar graph is mean ± 95% CI). (B) Dendritic bleb analysis indicated no significant changes between wild-type and GluN2D-A678D. (C) Confocal images display morphological features of cultured rat cortical neurons transfected with GFP-N1 and either wild-type GluN2D (left) and GluN2D-A678D (right), respectively. Note the presence of cellular debris in the mutant-transfected cells (asterisk), indicative of toxicity and as quantified in A. Scale bars = 20 μm. Experiments were repeated in four independent culture dates.