Fig. 4.
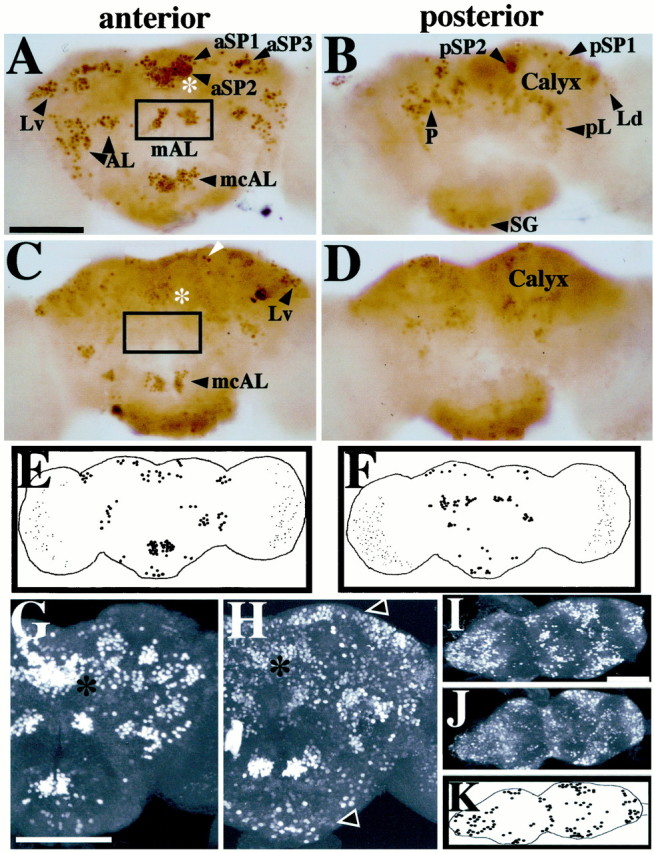
Nonrandom spatial effects offru1 on expression of FRUM in the brain. Pupal progeny of males heterozygous for this (recessive sterilizing) mutation had CNSs dissected (from 2-d-old pupae) and subjected to whole-mount anti-FRUM histochemistry. A,B, Control brightfield micrographs (from PhotoShop assemblies of four to five consecutive focal-plane images each) obtained from a wild-type (WT) brain, representative of 20 specimens stained by peroxidase-mediated color reactions (Fig. 3, compareA, B). C,D, fru1 anterior- and posterior-brain patterns, respectively, from scrutiny of 12 mutant specimens (processed and photographed as in A andB). Only a few cells with low-intensity staining were detected within the fru-aSP1 and fru-aSP2 clusters of fru1 brains (asterisks, C vs A). C, The boxed area designates the absence of the normally stained fru-mAL cluster (cf. box in A). Certain neurons showed no apparent staining-intensity decrement compared with WT; this is exemplified by neurons pointed to byarrowheads in C (also seeE and F). Other FRUM cells or clusters were absent or exhibited significantly decreased staining intensities in this mutant, e.g., in the vicinity of the mushroom-body calyx(D); these qualitative and quantitative anomalies of sex-specific fru expression are consistent with those obtained by in situ hybridizations using later-stagefru1 pupae (Goodwin et al., 2000).E, F, Diagrams of representative anterior and posterior fru1 brain views, respectively, showing cells or clusters with relatively strong staining intensities in brain regions that apparently correspond to those expressing FRUM in WT. G,H, Confocal images showing, respectively, anterior views of 2-d-old male pupal brains from WT andfru1 males (representative of 36 and 7 specimens, respectively, processed in this manner for animals of the two genotypes). Asterisks denote the location of the nearby fru-aSP1 and fru-aSP2 clusters that exhibit subnormal numbers and intensities of stained neurons infru1(H). Brains from this mutant also contain FRUM immunostaining in regions not labeled in WT. Such ectopic signals in fru1 are widely distributed and show low-intensity staining.Arrowheads point to examples of such ectopic-expression regions. I, J, Confocal images showing ventral views of ventral nerve cords dissected from WT andfru1 2-d-old male pupae.K, Diagram of FRUM-containing VNC neurons that gave relatively high-intensity staining. These cells are in posterior CNS regions that apparently correspond to the locations of such neuronal groups, although numbers of signal-containing cells are reduced within a given VNC region of the mutant. Scale bars, 100 μm.
