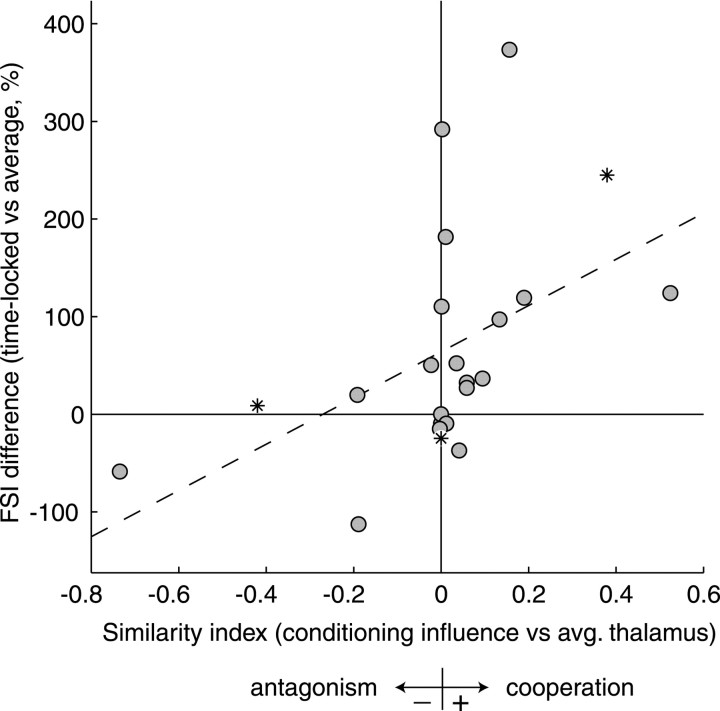
Fig. 6.
Relationship between the cooperativity of conditioning influence and the difference in feature selectivity for potentially causal spikes. The similarity index for the conditioning influence and the average thalamic STRF indicates the degree of cooperation (positive values) or antagonism (negative values). The FSI difference between time-locked, potentially causal spikes and average spikes quantifies how much more or less stimulus information the time-locked spikes carry. Similarity index and FSI differences are significantly and positively correlated (r = 0.50; 0.01 <p < 0.02). The dashed line is the best fit in a least mean squares sense. Asterisks are pairs from Figures 4 and 5. Cooperative conditioning influences tend to increase the feature selectivity of time-locked spikes, and antagonistic conditioning tends to decrease it.