Fig. 1.
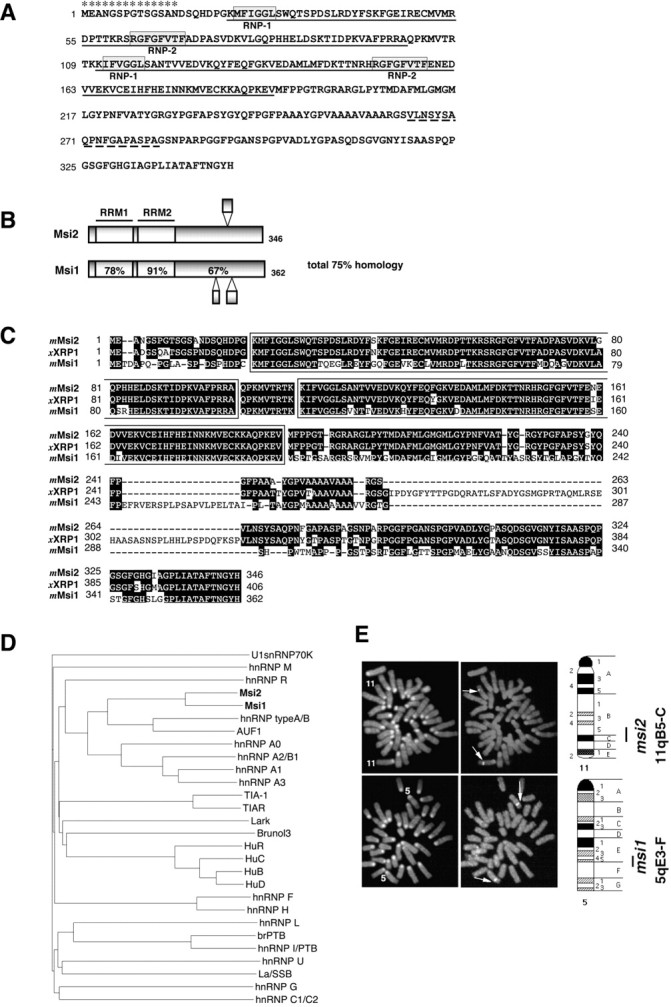
Primary structure and chromosomal localization of Msi2 and Msi1. A, The deduced amino acid sequence of mouse Msi2 protein. The two RNA recognition motifs areunderlined. Each RRM includes two highly conserved sequences designated RNP-1 and RNP-2(boxed sequences). The broken underlinesindicate the regions that are missing in the form arising from alternative mRNA splicing. Asterisks denote the peptide sequence used as an immunogen to generate anti-Msi2 antibody.B, Domain structures of the mouse Msi2 and Msi1 proteins. The percentages of amino acid identity between Msi1 and Msi2 within each RRM and in the C-terminal half are shown. Bulged small boxes represent the regions arising from alternative splicing. C, Amino acid sequence alignment of mouse Msi2 with its known homologs, Xenopus RNA-binding protein (XRP1), and mouse Msi1. The two RRMs are boxed, and gaps in the alignment are indicated by dashes. Amino acid residues conserved in more than two proteins are shaded.D, Dendrogram showing a multiple sequence comparison of various mammalian RRM-containing RNA-binding proteins. Sequences derived from selected proteins were compared using the clustalW program on the DDBJ www server. The branch lengths are proportional to the differences between sequences. The accession numbers of each protein are given in Materials and Methods. E, Chromosomal localization of the mouse msi1 and msi2genes by FISH. The left panels show metaphase chromosomes stained with DAPI for the identification of individual mouse chromosomes. Chromosomes 11 and 5are numbered. The right panels represent the same metaphase chromosomes with the hybridization signals from themsi2 (top panels) and msi1(bottom panels) genes (arrows indicate each signal). The closed bars on the right side of each ideogram indicate the possible location of the msi2 andmsi1 genes.
