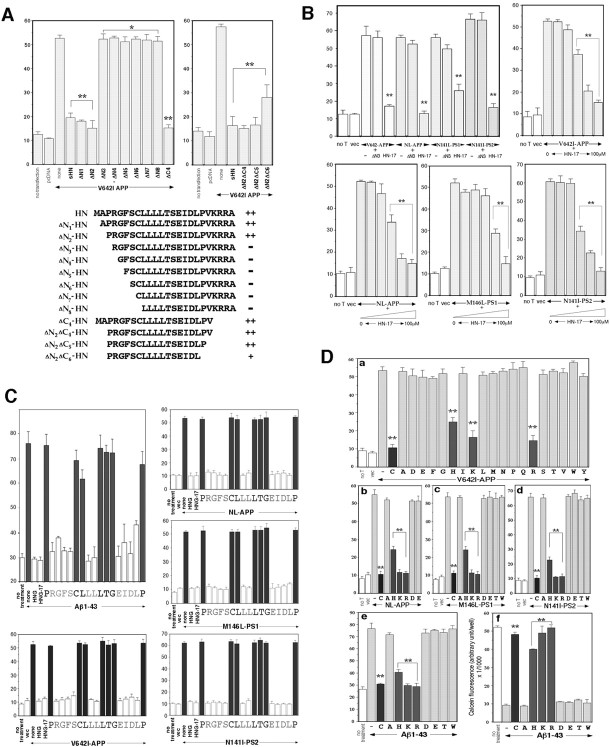
Fig. 4.
Detailed structure–function relationship for the rescue activity of HN. A, Effects of truncated HN derivatives on neuronal cell death by V642I-APP. F11 cells were transfected with V642I-APP cDNA in the presence or absence of each synthetic HN derivative (10 μm) for 72 hr, and cell mortality was similarly measured by trypan blue exclusion assay. Thetop left panel indicates the results of the examination in which the indicated N-terminally truncated peptides of HN were investigated. The top right panel indicates the results of the examination in which the indicated C-terminally truncated peptides of ΔN2 HN were investigated. The results obtained from the experiments shown in the panels are summarized in thebottom panel. ++, Strong suppression without significant differences from suppression by authentic HN; −, little suppression of cell death without significant differences from cell death by V642I-APP alone; +, intermediate suppression with significant differences from both V642I-APP alone and V642I-APP plus sHN. The vertical axis in all panels represents percentage of dead cells of total cells. B, Effects of ΔN3 HN and HN-17 on neuronal cell death by four representative FAD genes. F11 cells were transfected with V642I-APP, NL-APP, M146L-PS1, or N141I-PS2 cDNA in the presence or absence of 10 μm ΔN3 HN or 10 μm HN-17 for 72 hr, and cell mortality was similarly measured (top left panel). In otherpanels, the dose–response curves of the HN-17 effects for suppression of neuronal cell death by the four FAD genes are indicated. F11 cells were similarly transfected (Figure legend continued.) with each FAD gene in the presence or absence of increasing concentrations (0, 10 nm, 100 nm, 1 μm, 10 μm, and 100 μm from left toright) of HN-17 for 72 hr, and cell mortality was measured. In each series of experiments, cell mortality without transfection (no T) or with pcDNA transfection (vec) was measured as controls. ** and * inA and B indicate significant and not significant versus relevant FAD gene transfection, respectively.C, Effects of Ala-scanned HNG-17 on neuronal cell death by four representative FAD genes and Aβ1–43. Primary neurons were treated with 25 μm Aβ1–43 (top left panels) or F11 cells were transfected with each of V642I-APP, NL-APP, M146L-PS1, or N141I-PS2 cDNA (other panels) in the presence or absence of 10 nm Ala-substituted HNG-17 for 72 hr, and cell mortality was similarly measured. In this figure, cytoprotective effects were elicited by each Ala-substituted HNG-17 whose substituted residue was shown under the value of cell mortality. For instance (top left), when neurons were incubated with 25 μm Aβ1–43 in the presence of 10 nmARGFSCLLLLTGEIDLP (A is substituted fromP) for 72 hr, the cell mortality was 75.3 ± 4.4% (mean ± SD of three independent experiments), which was comparable with the mortality by Aβ1–43 incubation (76.1 ± 4.7%). When neurons were incubated with 25 μm Aβ1–43 in the presence of 10 nm HNG or HNG-17, the cell mortality was 29.3 ± 0.9 or 28.8 ± 1.3%, respectively, which was comparable with the basal mortality (30.0 ± 1.6%, shown asno treatment). When an Ala-substituted HNG-17 indicated drastic loss of neuroprotective activity, the correspondingcolumns are stained black. All values in these figures indicate means ± SD of three independent experiments. D, Effect of Cys8substitution on the rescue activity of HNG. a, F11 cells were transfected with or without V642I-APP cDNA (1 μg) and treated with each (10 nm) of the HNG mutant peptide whose Cys8 was substituted to one of the all 19 possible amino acid residue (indicated by one single letter). Cell mortality was measured 72 hr after the onset of transfection. The cell mortality above each letter represents the result of each experiment in which cells transfected with V642I-APP were incubated in the presence of 10 nm HNG with Cys8 substitution to the indicated amino acid residue. no T implies no transfection, andvec means empty pcDNA transfection without peptide treatment. C indicates authentic HNG. All values indicate means ± SD of three independent transfections.b–d, F11 cells were transfected with or without FAD gene (b, NL-APP; c, M146L-PS1;d, N141I-PS2) and treated with each (10 nm) of the HNG mutant peptide whose Cys8 was substituted to the indicated amino acid residue. Cell mortality was similarly measured 72 hr after the onset of transfection. All values indicate means ± SD of three independent transfections. e,f, Primary neurons were treated with 25 μmAβ1–43 in the presence of each (10 nm) of the HNG mutant peptide whose Cys8 was substituted to the indicated amino acid residue. The induced neurotoxicity was measured by trypan blue exclusion assay (e) and by calcein viability assay (f) 72 hr after the onset of Aβ treatment. All values indicate means ± SD of three independent transfections (a–d) or three independent treatments (e, f). ** indicates significant versus relevant FAD gene transfection (a–d) or Aβ treatment (e, f).