Fig. 3.
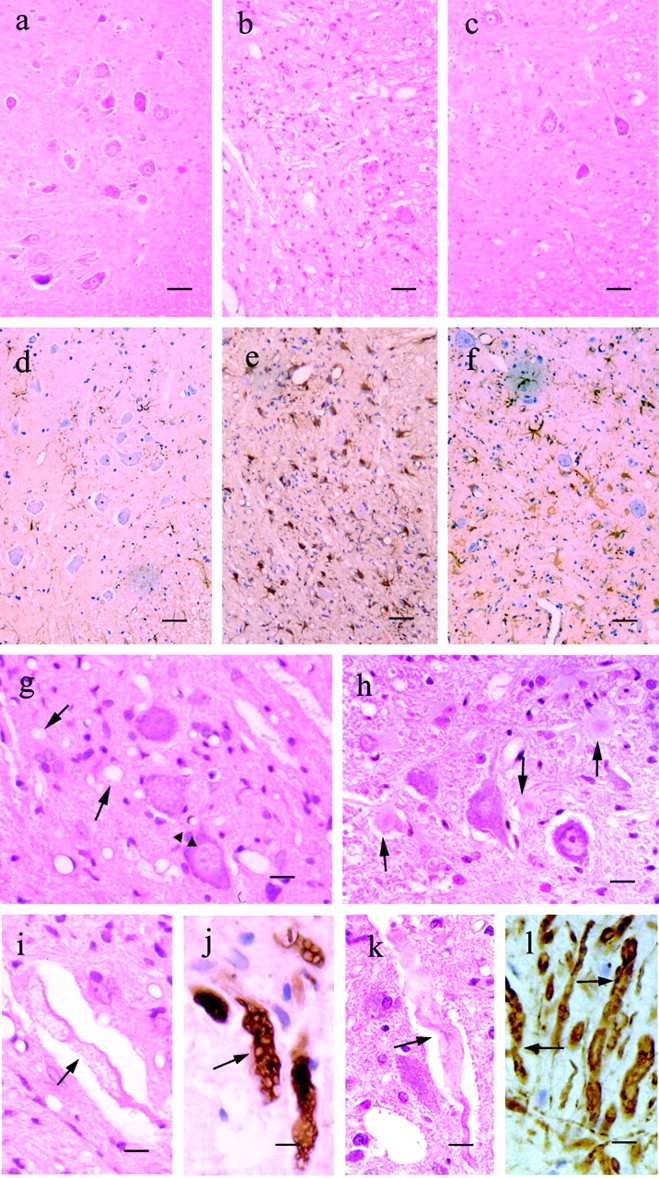
Major histopathological findings in the G93A-39 and H46R-4 transgenic rats. a–f, Ventral horns of the lumbar spinal cord from a 6-month-old normal littermate(a, d), a G93A-39 transgenic rat at 4.5 months (b, e), and an H46R-4 transgenic rat at 6.0 months (c, f). Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (a–c) and immunostained using GFAP (d–f). g, h, Higher magnification views of the neuropil in the ventral horn of the lumbar spinal cord in G93A-39 (g) and H46R-4 (h) transgenic rats. g, Conspicuous vacuoles in the neuropil (arrows) and perikarya of motor neuron (arrowheads) are indicated in the G93A-39 transgenic rat section. h, Lewy body-like inclusions are readily apparent (arrows) in the neuropil of the H46R-4 transgenic rat. i, Axonal swelling and vacuolation in the G93A-39 transgenic rat. j, Phosphorylated neurofilament is identified using antibody SMI-31 in the G93A-39 rats. k, Swollen and tortuous ventral axon in H46R-4. l, Phosphorylated neurofilaments are also identified with antibody SMI-31 in the H46R-4 rats. Ini–l, the arrows designate axons. Scale bars: a–f, 50 μm;g, h, 20 μm;i–l, 10 μm.
