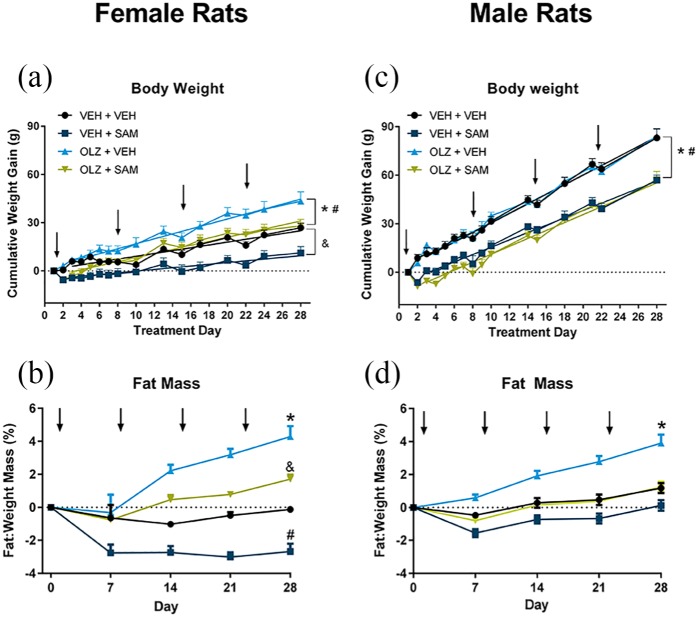
Figure 2.
OLZ (100 mg/kg, subcutaneous (s.c.)) and SAM (female: 16 mg/mL or male: 50 mg/mL; delivered at 2.5 μL/h, s.c. infusion) alone or in combination were administered for 28 days. (a) Female rats; OLZ administration produced a statistically significant increase in the rate of weight gain versus control (*p < 0.001). SAM alone decreased the rate of weight gain versus vehicle (**p < 0.01). Co-administration of SAM decreased the effects of OLZ on weight (#p < 0.05). (b) Female rats. OLZ produced a significant (*p < 0.001) increase in adipose accretion versus vehicle control by day 28. SAM alone decreased adipose accretion (#p < 0.001) while co-administration of OLZ + SAM was similar to vehicle control by day 28. (c) Male rats; OLZ administration did not change the rate of weight gain significantly versus vehicle control. Addition of SAM decreased the rate of weight gain in both vehicle (*p < 0.001) and OLZ (#p < 0.01) treated rats. (d) Male rats; OLZ administration produced a significant increase in adipose accretion versus vehicle control by day 28 (*p < 0.01). Co-administration of OLZ + SAM was similar to vehicle control at day 28. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Arrows indicate time of OLZ injection.
OLZ: olanzapine; SAM: samidorphan; VEH: vehicle