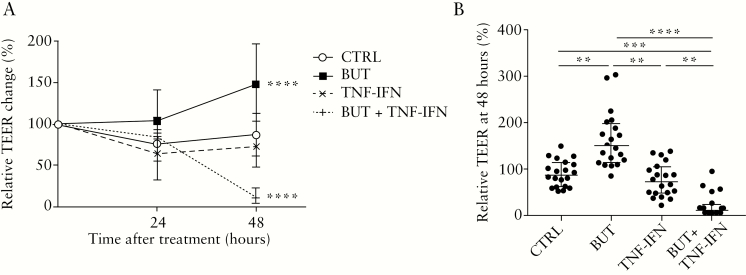
Figure 2.
Effect of butyrate ± TNFα and IFNγ on TEER in monolayer cultures of UC patients [n = 10] and non-UC controls [n = 10] during the whole treatment period [A] and at the end of treatment [B].[A] Complementation with butyrate ± TNFα and IFNγ induced significant changes in TEER over time compared with the untreated control condition [two-way ANOVA, p <0.0001]. [B] At 48 h, treatment had a significant effect on TEER [Friedman test, p <0.0001] with higher values for the cells treated with butyrate compared with all others, but butyrate had the opposite effect in the presence of TNFα and IFNγ as inflammatory mediators compared with all other treatment conditions [Dunn tests, adj.p <0.05]. TEER is given as percentage change to the initial values of the cultures at the start of treatment [0 h]. Data from UC patients and non-UC controls were merged for analysis. Data are shown as medians with interquartile ranges. Each treatment condition was tested in duplicate. Significant comparisons of the post-hoc tests are indicated. TEER, transepithelial electrical resistance; UC, ulcerative colitis; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; IFN, interferon; ANOVA, analysis of variance; CTRL, negative control [medium]; BUT, 8 mM butyrate; TNF-IFN, 25ng/ml TNFα and 25ng/ml IFNγ; BUT + TNF-IFN, 8 mM butyrate + 25ng/ml TNFα and 25ng/ml IFNγ. **adj.p <0.01; ***adj.p <0.001; ****adj.p <0.0001.