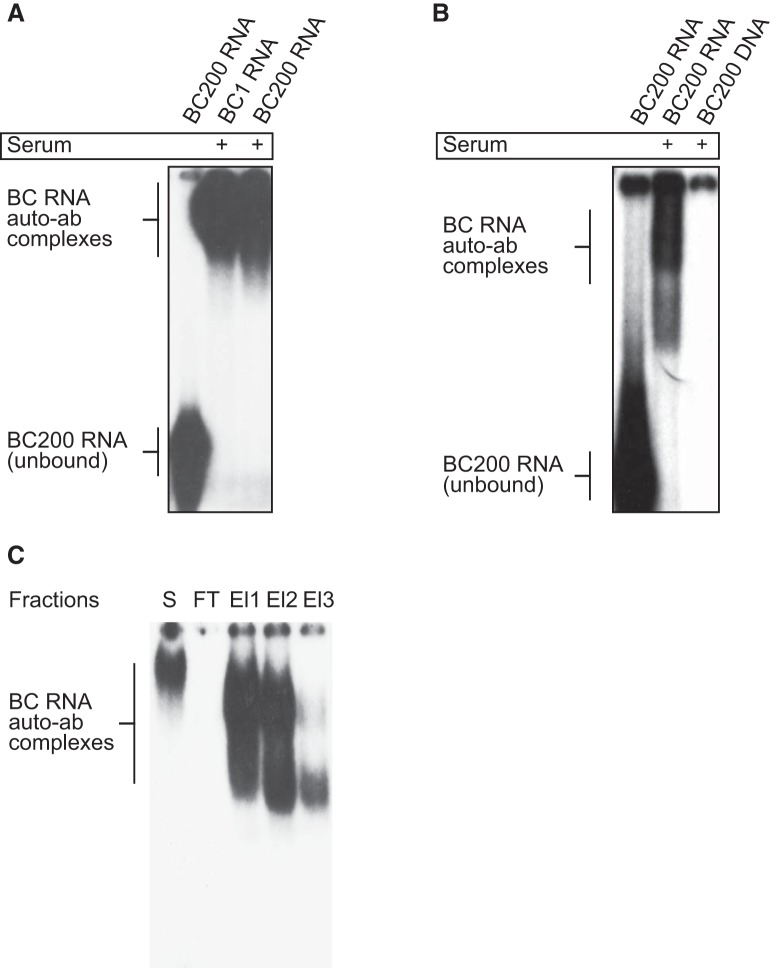
Figure 2.
SLE autoimmune responses to BC RNAs. A, 32P-labeled BC1 and BC200 RNAs were used in In EMSA analysis. RNAs bound in immune complexes were resolved from unbound RNAs by PAGE. BC1 and BC200 RNAs formed complexes with serum components from an SLE patient. B, The same serum was found nonreactive to BC200 DNA. Serum used in the experiments shown here was from SLE patient S1 (see below for patient codes). C, After antibody purification from serum (S) using Protein G, flow-through (FT) and three stepwise elution fractions (El1, El2, El3) were tested for anti-BC RNA reactivity by EMSA. While no reactivity was detected in FT, strong reactivity was apparent in E1 and E2 and weak reactivity was observed in E3. In this and the following figures, SLE autoantibodies are identified by patient codes in which a number may be preceded by the letters S (indicating an SLE patient with a history of seizures) or OBS (indicating an SLE patient with organic brain syndrome). SLE patients with no history of seizures or OBS are identified by numbers without preceding letters. See also Materials and Methods.