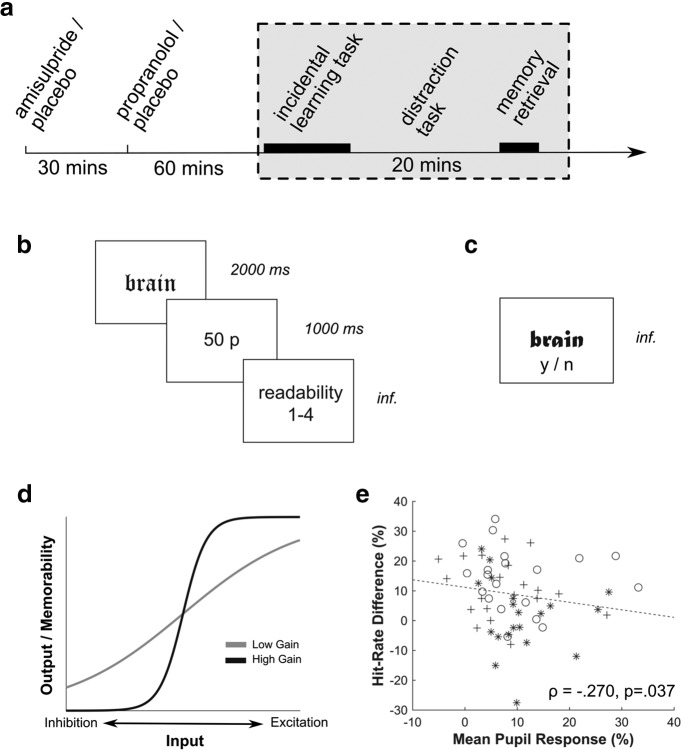
Figure 1.
Neural gain during incidental episodic memory. a, To assess specific effects of dopamine and noradrenaline, we administered either amisulpride or propranolol before an incidental learning task in a placebo-controlled design. Subjects were probed with a recognition task (c) ∼20 min after performing an incidental-learning task (b). b, Incidental learning phase: subjects rated readability of common words, presented in two different fonts. Twenty-five percent of the words were randomly rewarded £0.50 to boost arousal (“50 p” or “00 p” feedback after word presentation). c, Memory recognition test: subjects were asked to indicate whether a word has been shown during the first phase. Half of the words were presented in a different font compared with the original presentation (switch-font condition). d, Predictions of neural gain. Neural gain is assumed to modulate how information is processed along neural populations. Under high neural gain (black), relevant features (such as the word shape in our experiment) are prioritized and their representation strengthened while unimportant features (here: word meaning) will be suppressed. Under low neural gain (gray), both relevant and negligible features are represented increasing the likelihood that both word shape and semantics will be stored in memory. e, Pupil response indicates neural gain effects. Across all groups, we replicate our previous finding that pupil response during learning (as indirect indicator of neural gain) is linked to memory performance. Subjects with low pupil response (indicating high gain) show a stronger memory selectivity bias with a worse performance after a font switch (compared with a presentation in the same font; measured by hit rate). Subjects with larger phasic pupil response (indicating low gain) show less memory bias between same and switch-font condition. Shaded area in a: time period of likely drug effect. inf, Unlimited response time; ○, placebo, +, propranolol, *, amisulpride.