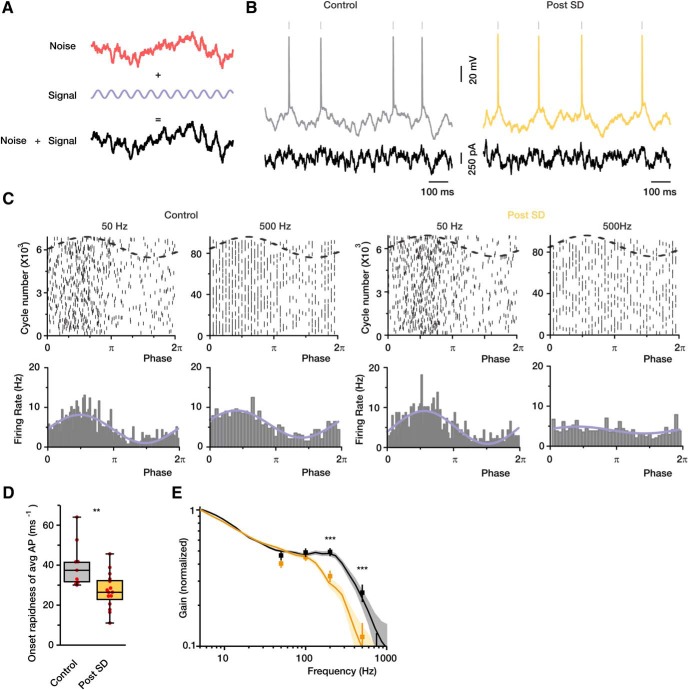
Figure 2.
The encoding capabilities of cortical neurons are reduced following SD. A, Experimental paradigm for testing the encoding capabilities of cortical neurons. For every neuron, a current command containing signal (sinewave) and variable fluctuating background (noise) was synthetized and delivered via the somatic whole-cell pipette. B, Noisy voltage fluctuations and APs elicited by somatic current injection of the noise plus signal function. C, Raster plots of AP times (top) and firing rates (bottom) as a function of the phase of the sinewave. Control and recovered neurons were injected with synthetic currents containing either 50 or 500 Hz sinewave component. The firing rate of the recovered neurons is not affected by the 500 Hz sinewave. D, AP onset rapidness of control (gray) and recovered (yellow) neurons (n = 9 and n = 15, respectively). E, Vector strength and dynamic gain of neuronal responses as a function of input frequency. Pooled data from control and recovered neurons are shown (n = 9 and n = 13 neurons, respectively). Box charts represent median (horizontal line), 25th–75th percentile (box), and extremes. Faded error bars indicate 5%–95% CIs of bootstrapped data (1000 repetitions). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.