Figure 3.
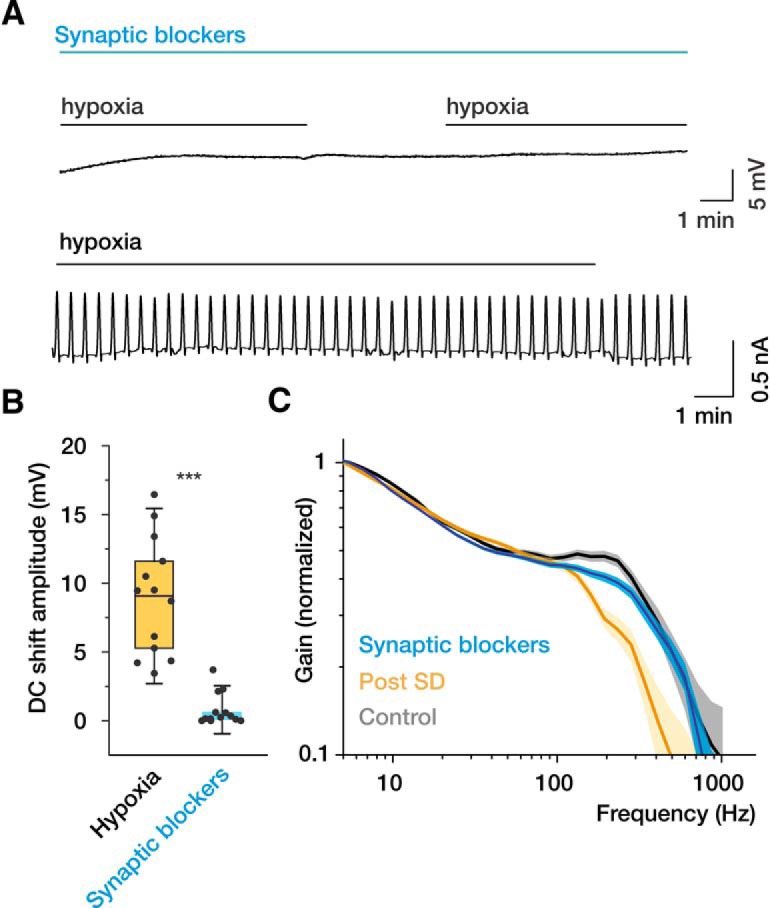
Ionotropic glutamate receptor blockers prevent SD and preserve the high-frequency encoding of the neurons following hypoxia. A, In the presence of the glutamate receptor blockers APV (50 μm), MK-801 (50 μm), DNQX (50 μm), and the GABAA receptor blocker BMI (25 μm), hypoxia fails to generate SDs (extracellular recording, top) and SD current (whole-cell voltage-clamp recording, bottom). B, Quantification of hypoxia-induced DC shift amplitudes in aCSF and in the presence of ionotropic glutamate receptor blockers. C, In the presence of synaptic blockers, hypoxia has little effect on the dynamic gain of recovered neurons (blue curve, data pooled from 14 neurons). Faded error bars indicate 5%–95% CIs of bootstrapped data (200 repetitions). The dynamic gain curves of control (gray) and recovered (yellow) neurons (Fig. 2) are shown for comparison. Box charts represent median (horizontal line), 25th-75th percentile (box), and standard deviation (bars). n = 13 slices with and n = 13 slices without synaptic blockers. ***p < 0.001.
