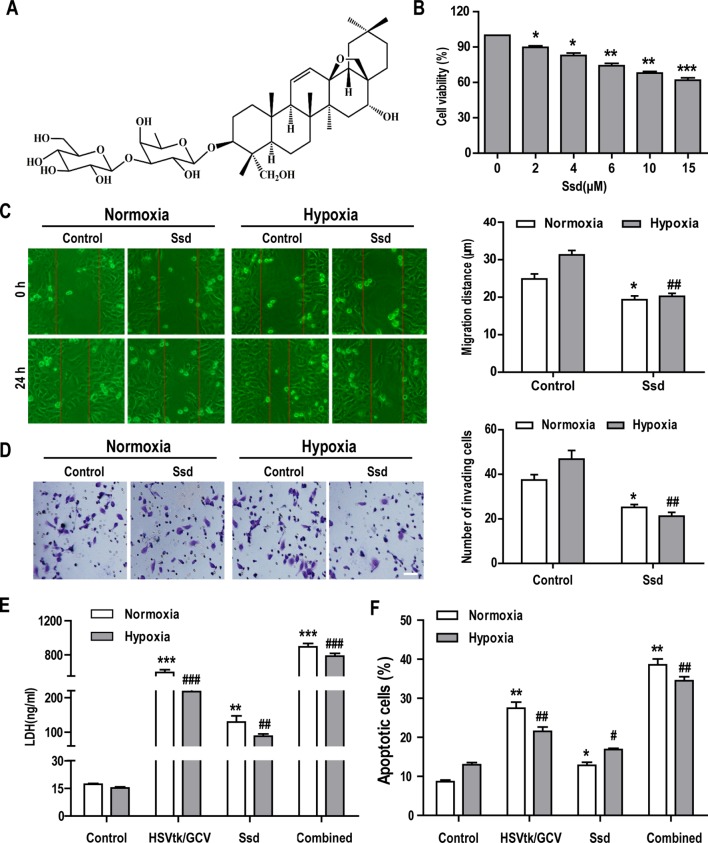
Figure 3.
Saikosaponin-d (Ssd) markedly inhibits the malignant phenotype in Hep3B cells and increases their sensitivity to chemotherapy under hypoxic conditions. (A) Chemical structure of Ssd. (B) The viability of Hep3B cells treated with different concentrations of Ssd for 48 h was examined using the CCK-8 assay. (C) The effects of Ssd (6 µM) on the migration of Hep3B cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions were examined over 24 h by wound healing assay (scale bar, 50 µm). (D) The effects of Ssd on the invasive potential of Hep3B cells were examined by transwell assay under normoxic and hypoxic conditions (scale bar, 50 µm). (E) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) expression in Hep3B cells was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) following exposure of cells to the indicated treatments. (F) Hep3B cell apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3); *P < 0.05, *P < 0.01, and *P < 0.001 when compared with the normoxia control; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, and ### P < 0.001 when compared with the hypoxia control (Student’s t test).