Figure 2.
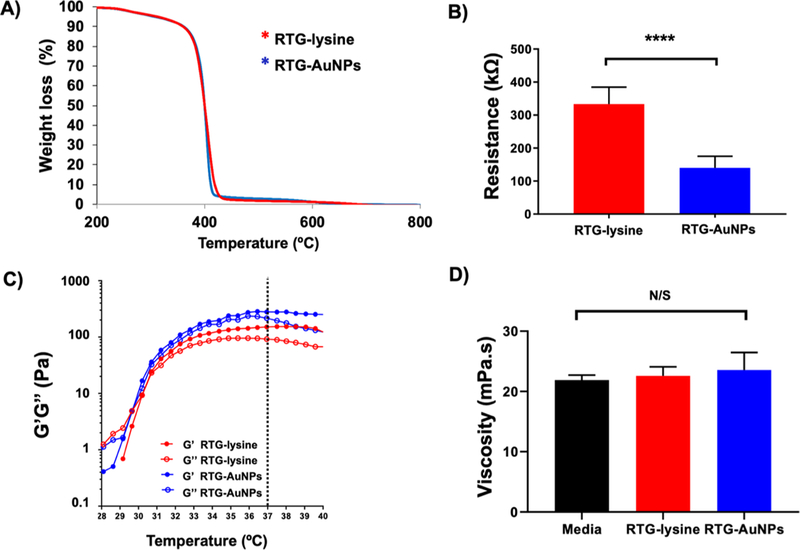
Characterization of the RTG-lysine and RTG−AuNP hydrogels. (A) A single weight loss monitored by TGA analysis demonstrates the chemical conjugation of the AuNPs to the RTG-lysine. (B) Resistance measurements demonstrating that the RTG−AuNP system is more conductive than the RTG-lysine system. p value: ****<0.0001. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (C) The RTG−AuNP system presents significantly higher mechanical properties to those of the RTG-lysine system. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (D) The viscosities of both the RTG−AuNP and RTG-lysine systems at 3% (w/w) concentration are similar to that of the NRVM cell culture media (N/S: non-significant). Data presented as mean ± S.D.
