Fig. 4.
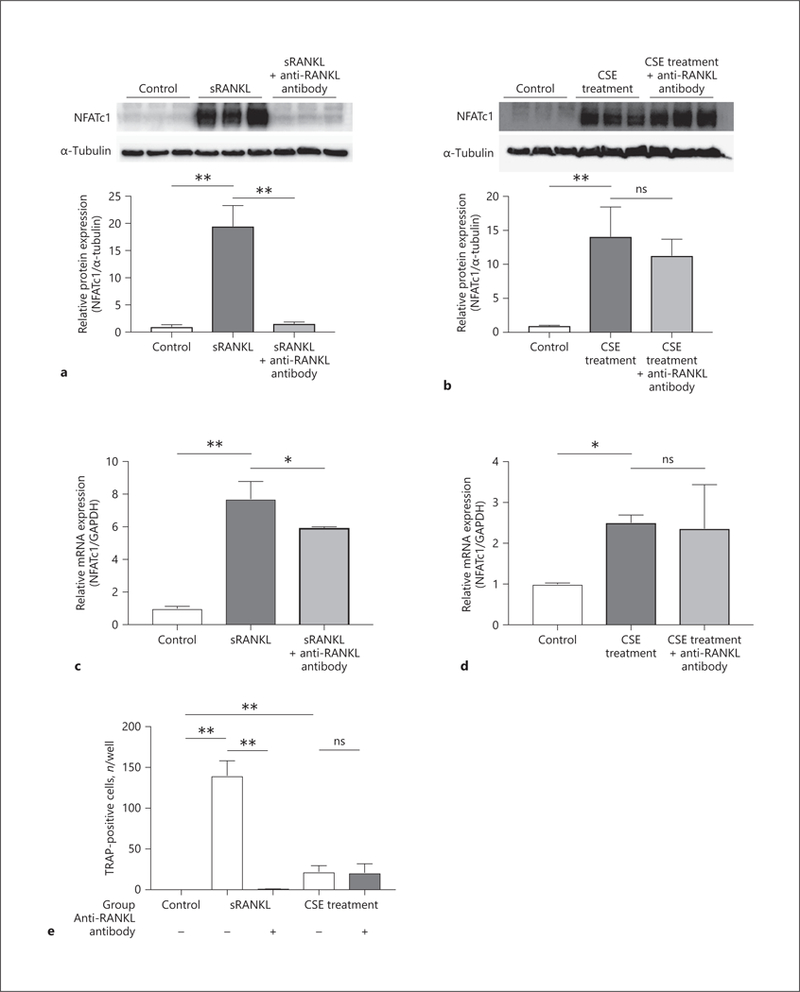
Effect of anti-RANKL neutralizing antibody on osteoclastogenic macrophage activation. To induce osteoclastogenesis, RAW 264.7 cells were incubated in medium with 50 ng/mL of sRANKL or 2% CSE for 2 days. Furthermore, 100 ng/mL of anti-mouse RANKL neutralizing monoclonal antibody was added to inhibit the RANKL-RANK pathway. By Western blotting analysis, the protein expression levels of NFATc1 were compared in the sRANKL treatment group (a) and CSE treatment group (b). NFATcl gene expression levels were evaluated in the sRANKL treatment group (c) and CSE treatment group (d). Macrophages were also cultured and stimulated by sRANKL or CSE with or without anti-RANKL antibody for 5 days, and the number of TRAP-positive macrophages was counted (e). Values are presented as means ± SD for at least 3 replicates. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. ns, not significant; RANK, receptor activator of NF-κB; RANKL, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; sRANKL, soluble RANKL; CSE, cigarette smoke extract; NFATc1, nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1; TRAP, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase; SD, standard deviation.
