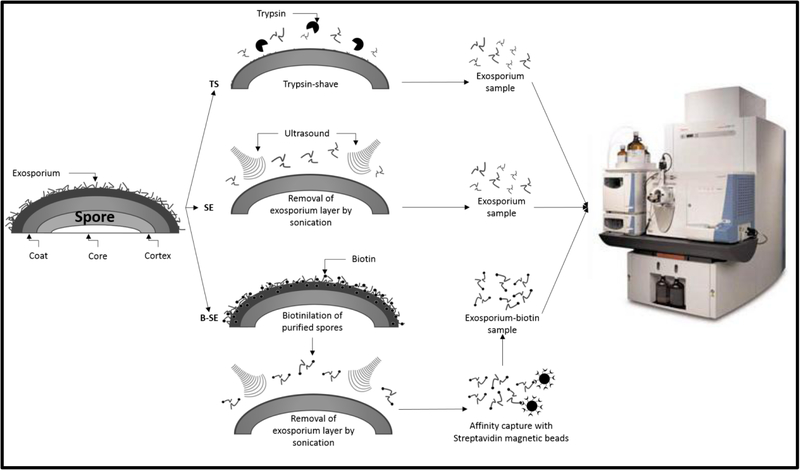
Figure 1. Gel-free strategy to remove and identify exosporium-like layer proteins of C. difficile 630 spores.
Experimental gel-free strategy to determine the proteome of the exosporium-like layer of C. difficile 630 spores. i) C. difficile spores were trypsin-digested (TS) for 18 h at room temperature and peptides analyzed by MS/MS as described in Methods section: ii) The exosporium-like layer of C. difficile 630 spores was removed by sonication, digested with trypsin and peptides analyzed by MS/MS; iii) C. difficile 630 spore surface proteins were biotin-labeled prior to sonication, and biotin-labeled exosporium extracts were captured by Streptavidin-magnetic beads and digested with trypsin and peptides were identified by MS/MS. All experiments were done with two biological replicates.