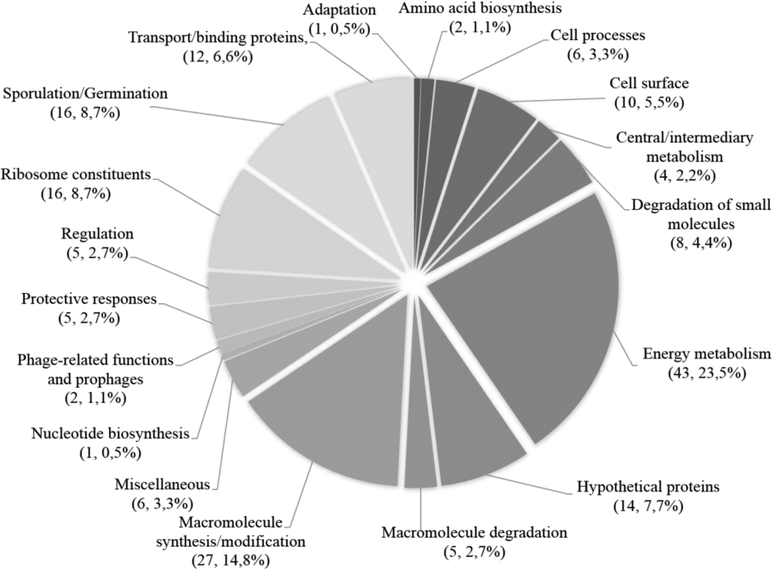
Fig. 3. Representation of the distribution and abundance by functional classes of the exosporium proteins of C. difficile spores.
Shown is the percentage of each functional class in the exosporium of C. difficile 630 spores (Functional classes are described in reference27). The elevated number of energy metabolism and cytosolic proteins identified in this spore layer are most likely vegetative cell contaminants entrapped during the assembly of the exosporium layer, and therefore, it is likely unlikely that these proteins are genuine exosporium proteins.