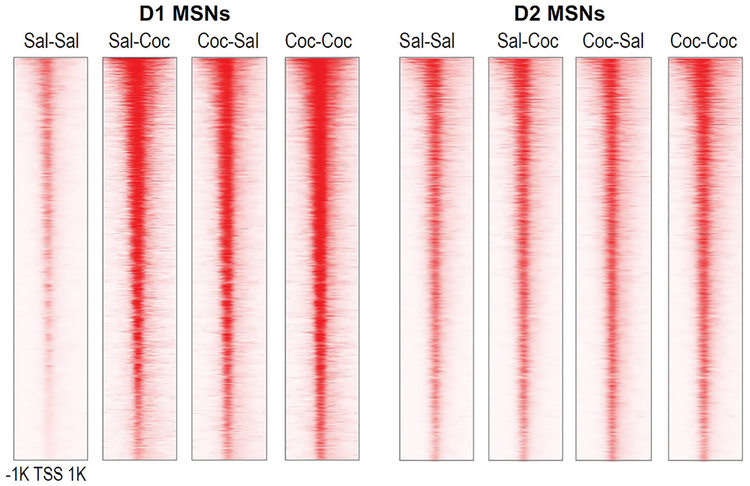
Figure 4.
Cell type–specific control of chromatin accessibility in NAc by acute and chronic cocaine exposure. ATAC-seq was performed on D1 and D2 MSNs isolated from NAc using FACS in two transgenic mouse lines that express EGFP-RPL10a in either subtype (Drd1a/Drd2a::EGFP-L10a). Each horizontal row reflects a single gene locus centered around its TSS and 1 kb up- and downstream. This ongoing study investigates immediate and long-term changes in chromatin architecture, following acute cocaine (Sal-Coc, 1 h after 20 mg/kg cocaine by intraperitoneal injection) and prolonged withdrawal after chronic cocaine exposure (Coc-Sal, 30 d following 10 d of cocaine injections) as well as after drug challenge in withdrawal animals (Coc-Coc, 1 h after cocaine challenge). Drug-induced changes in chromatin accessibility discriminate D1 from D2 MSNs, and D1-specific chromatin “opening” following chronic cocaine exposure is sustained even during prolonged periods of withdrawal.