Figure 3.
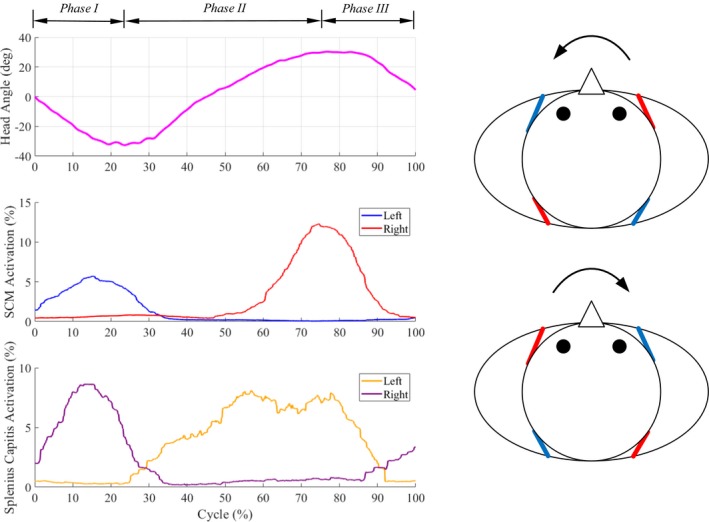
Single plane axial rotation (Movie S2). (left) Motion (primary head angle) and EMG patterns of neck muscles of a healthy subject during a movement cycle. (right) Axial rotation is caused by a contralateral pair of muscles. For example, the simultaneous actuation of left SCM rope and right SC rope results in right axial rotation. The arrows indicate the directions of motion, blue (inactive) and red (active) lines indicate the activation of corresponding muscles during motion.
