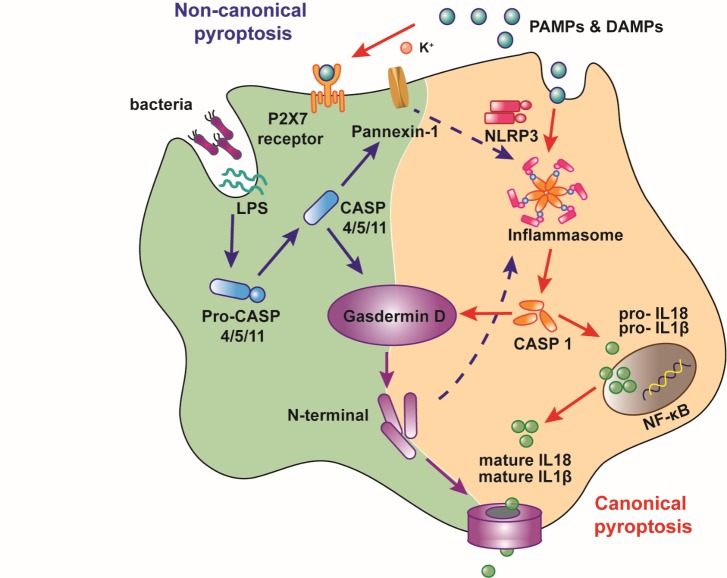
Figure 1.
Pathways of pyroptosis. There are two different pyroptotic pathways. The canonical pyroptosis is dependent on the activation of caspase-1 by inflammasomes, which can recognize PAMPs and DAMPs. Compared to canonical pyroptosis, noncanonical pyroptosis is mediated by the activation of caspase-1 and caspase-4/5 (caspase-11 in mice), which can be directly activated by LPS independent of TLR4. Upon activation, these caspases cleave gasdermin D then bind to lipids in the plasma membrane and form oligomeric pores leading to the release of cellular contents and cell death. Caspase-4/5/11 activates the Pannexin-1 channel and then opens the P2X7 pore to mediate pyroptosis. Meanwhile, activation of caspase-1 results in the cleavage of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 and the production of mature cytokines. PAMPS, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPS, damage-associated molecular patterns; IL-1β, Interleukin-1β; IL-18, Interleukin-18.