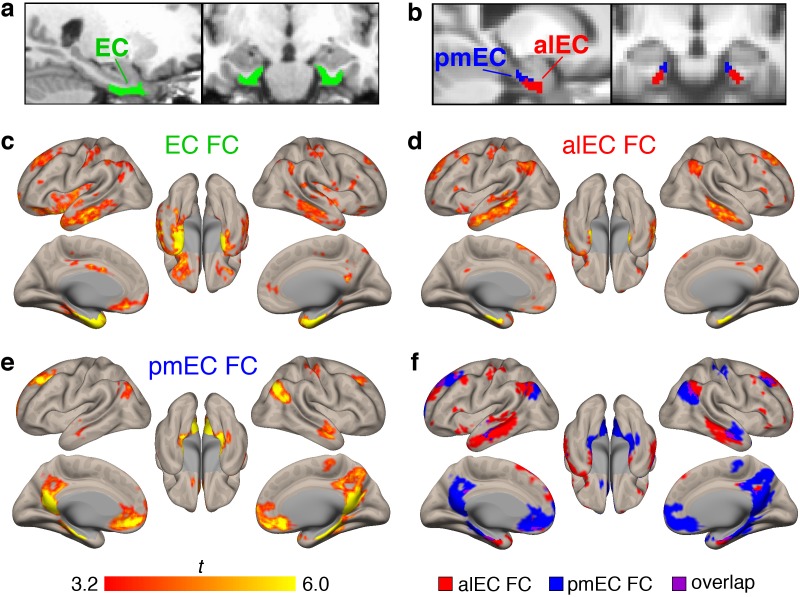
Figure 1. Functional connectivity (FC) of the different entorhinal seeds in healthy young adult (YA) participants.
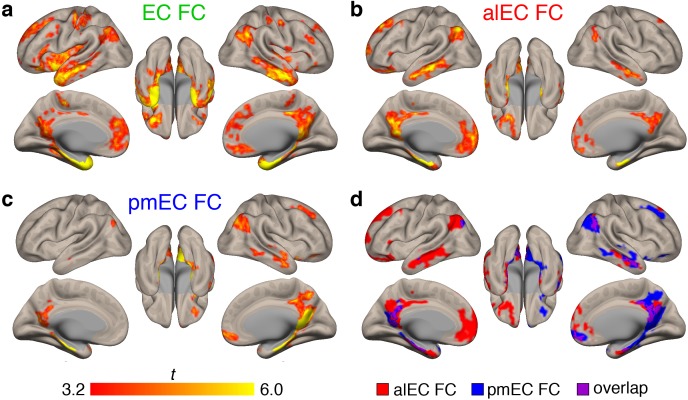
(a) The full entorhinal seed (EC, green), including transentorhinal, lateral, and medial regions, was derived from FreeSurfer segmentation of each participant’s native space T1, and time series were extracted from native space fMRI data. (b) The anterolateral EC (alEC, red) and posteromedial EC (pmEC, blue) seeds were applied in template space, and time series were extracted before smoothing to preserve the spatial resolution of the seeds. (c–e) Seed-to-voxel FC analyses were performed for each seed with semi-partial correlations. Group level FC results were derived from one-sample t-tests controlling for age and sex, and thresholded at the voxel (p<0.001 uncorrected) and cluster level (p<0.05, FDR corrected). Results reflect t-statistics. (c) FC of the EC seed included medial temporal, lateral temporal, and limbic regions. (d) FC of the alEC seed included anterior temporal regions, such as medial and lateral temporal lobe. (e) FC of the pmEC seed included posterior medial regions, such as the parahippocampal gyrus and posterior cingulate. (f) Binary maps of alEC (red) and pmEC (blue) FC show little spatial overlap (purple) between the FC patterns. See Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for parallel results using OA FC. See Figure 1—figure supplement 2 for a visualization of gray matter voxels removed due to signal drop out, and alEC and pmEC seeds overlaid on the group-mean functional image.