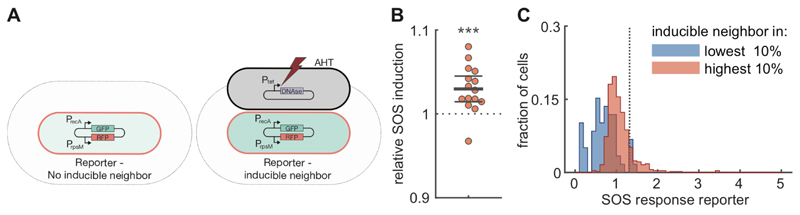
Figure 4. Direct cell-cell interactions in SOS response.
A) Test for direct interactions in SOS response. Cells with a transcriptional reporter for recA (pSV66-recA-rpsM, red cells) where grown together on agar pads with cells in which SOS response was induced by expressing the nuclease domain of colicin E2 (pSJB18, black cells). After 1h, the average SOS induction level was compared between reporter cells that do (right) and do-not (left) have inducible neighbors. The grey area indicates the region where cells are considered neighbors. Nuclease expression was induced by adding Anhydrotetracycline (AHT) to the agar pad. B). Cells neighboring inducible cells have higher SOS response levels. For each of 15 biological replicates, we measured the GFP intensity of a recA transcriptional reporter in cells with inducible neighbors (51-189 (mean=137) cells) and in cells with no direct inducible neighbors (359-713 (mean=575) cells). Each dot corresponds to a single biological replicate and shows the ratio between the mean GFP intensity in reporter cells next to inducible neighbors compared to the mean intensity in reporter cells without inducible neighbors. Points are horizontally offset, thick horizontal line indicates mean, thin lines 95% confidence intervals, over the 15 replicates. Reporter cells neighboring inducible cells have significantly higher levels of recA expression with a mean relative SOS induction of 1.030 (95% CI=1.015,1.045), p=9·10-4, t-test, n=15. C). Cells neighboring inducible cells with high levels of SOS response strongly upregulate their own stress response levels. Reporter cells (pUA66-recA) were mixed with inducible cells that also contained a recA transcriptional reporter (pSJB18 + pSV66-recA-rpsM) and grown together for 90 min on agar pads containing AHT. The distribution of SOS response levels is shown for reporter cells that are within 5μm of inducible cells with low levels (dimmest 10% of inducible cells, n=59 cells) of SOS response (blue) and for reporter cells that are within 5μm of inducible cells with high levels (brightest 10% of inducible cell, n=503 cells) of SOS response (red). The distributions were obtained by pooling the data of 4 biological replicates. The dashed vertical line indicates an SOS response level of 2 standard deviation above average. Distributions considering only direct neighbors are shown in Figure S9C.