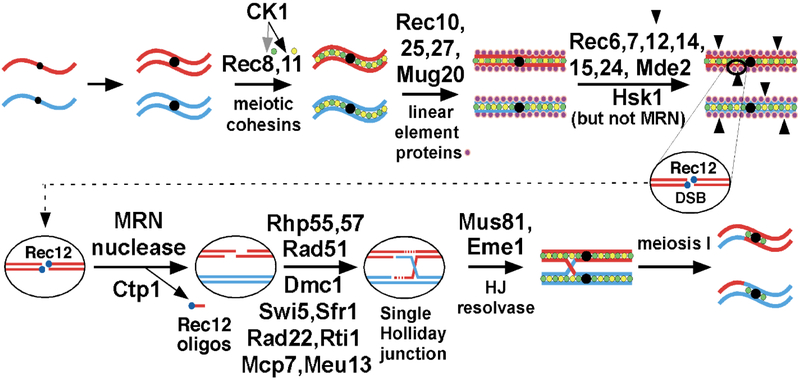
Figure 1. Pathway of meiotic recombination in S. pombe (modified from [93]).
Thick lines indicate the ds DNA of a chromatid, red for the chromosome from one parent and blue from the other parent; black dots indicate the centromeres. In ovals, thin lines indicate a single strand of DNA; dotted red lines indicate newly synthesized DNA. Accompanying replication, sister chromatid cohesins, containing the meiosis-specific subunits Rec8 and Rec11, are loaded onto chromosomes. In chromosomal arms casein kinase I (CK1; Hhp1 and Hhp2) phosphorylates Rec8, for its proteolysis and sister chromatid segregation, and Rec11, for its recruiting Rec10. Rec25, Rec27, and Mug20 direct Rec10 at high frequency to DSB hotspots. Rec10 binds Rec15, which with other indicated proteins activates Rec12 (Spo11 homolog) to make DSBs. The MRN complex and Ctp1 clip off Rec12 covalently bound to 5’ DNA ends and further resect the 5’ ends to produce long 3’-ended ss DNA tails. Rad51 and Dmc1 DNA strand-exchange proteins bind the tails and, with the additional proteins listed, form a displacement- (D-) loop with intact ds DNA. The D-loop (not shown) is cleaved to form a Holliday junction (HJ), which is resolved by the Mus81-Eme1 complex into crossover (shown) or non-crossover (gene conversion; not shown) products. HJ resolution is aided in an unknown way by Nse5 and Nse6, subunits of the Smc5-Smc6 complex [94]. Additional gene products required for meiotic recombination, but whose point of action remains unknown, include the following: mug1 (jnm1), mug5, pds5, rad54, rdh54, and rlp1; hop1 and mek1 [95], nse1 [96], pli1 [97], rec13, rec18, and rec21 [98], and rqh1 [99]. See [93] for references for genes not otherwise referenced here.