Figure 4.
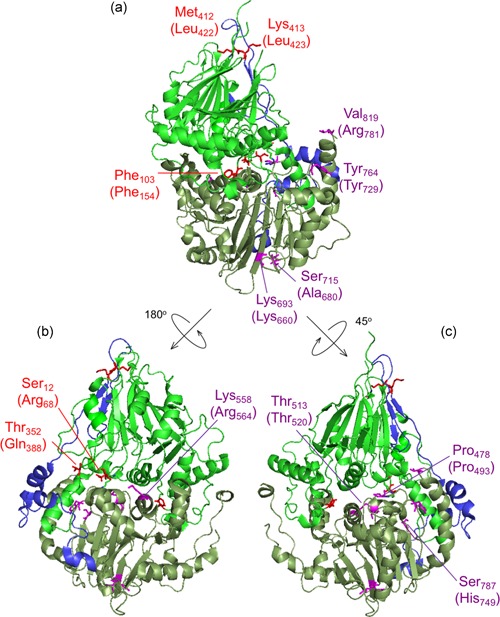
ELAC2 substitutions mapped on the structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNase Z. The structure of S. cerevisiae RNase Z (Trz1, PDB#5MTZ; Ma et al., 2017) is shown in cartoon using PyMol. The amino domain, inter‐domain linker, and carboxy domain are colored green, blue, and pale green, respectively. Three views are shown to effectively visualize all the substitutions. All 13 ELAC2 substitutions (3 published previously (Haack et al., 2013), and 10 novel) are shown in all three views. Residues are labeled with S. cerevisiae RNase Z numbers and the numbers in brackets are for the H. sapiens ELAC2 residues. Some residues are not conserved between S. cerevisiae and H. sapiens RNase Z. Residues Arg68, Phe154, Gln388 localized in the amino domain are marked in red; Leu422 and Leu423 are in linker (also marked in red); Pro493, Thr520, Arg564, Lys660, Arg680, Tyr729, His749, Arg781 are in the carboxy domain and indicated in purple. (a) View with amino domain up, carboxy domain down and linker behind with the H. sapiens residues Phe154, Leu422, Leu423, Lys660, Ala680, Tyr729 and Arg781 labeled. (b) The ELAC2 model is rotated with linker on left with the residues Arg68, Gln388 and Arg564 labeled. (c) ELAC2 rotated with linker on right and the residues Pro493, Thr520 and His749 labeled. Note: the residues at Arg68, Phe154, and Gln388 in H. sapiens ELAC2 map to the domain interface
