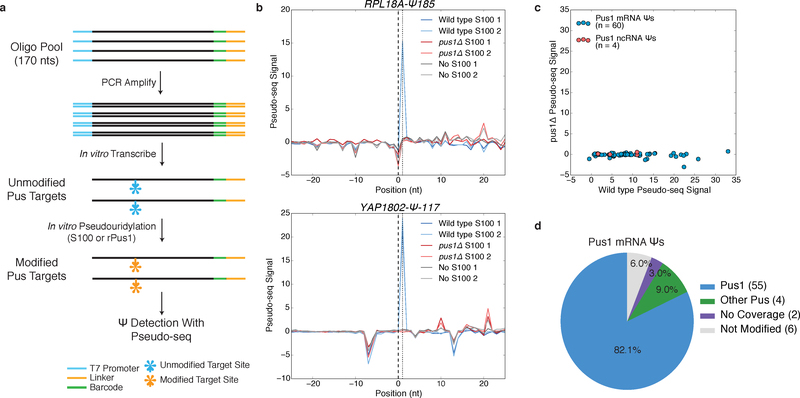
Figure 1: A High-Throughput In vitro Pseudouridylation Assay.
a) A schematic of in vitro pseudouridylation of oligo pool-derived RNAs and Ψ detection with Pseudo-seq. b) Pseudo-seq signal for mRNA substrates incubated with wild type S100 (blue), pus1Δ S100 (red), or no extract (gray). RPL18A-Ψ185 (upper), YAP1802-Ψ-117 (lower). c) A scatter plot of Pseudo-seq signal for pools incubated with wild type or pus1Δ S100 extracts. Sequences correspond to Pus1 ncRNA (red, n=4 sequences) and mRNA (blue, n=60 sequences) substrates. Values represent an average of n=2 replicates. d) Summary of in vitro pseudouridylation of PUS1-dependent mRNA Ψs.