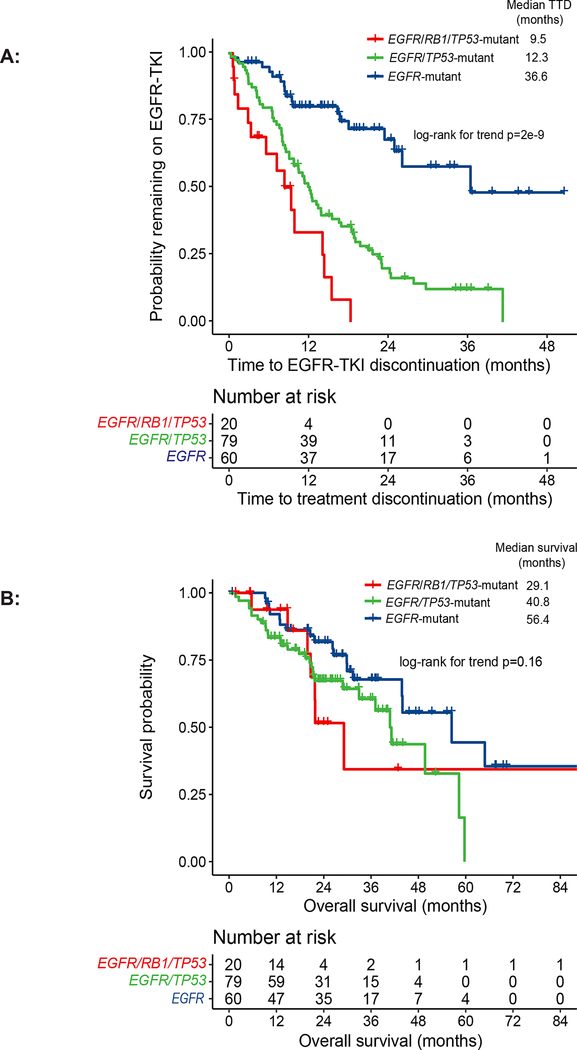
Figure 1.
Time to treatment discontinuation (TTD) and overall survival (OS) of patients with EGFR/RB1/TP53-mutant lung cancers: patients with EGFR/RB1/TP53-mutant lung cancer without baseline small cell lung cancer (SCLC) who were EGFR-TKI naïve at the time of next-generation sequencing (NGS) (n = 20) versus patients with EGFR/TP53-mutant RB1-wildtype (n = 79) and EGFR-mutant RB1/TP53-wild type lung cancer who were EGFR-TKI naïve at the time of NGS (A) The median TTD for patients with EGFR/RB1/TP53-mutant lung cancer was 9.5 months versus 12.3 months for EGFR/TP53-mutant RB1-wildtype (HR 2.0, 95% CI 1.1 – 3.6) versus 36.6 months in EGFR-mutant RB1/TP53-wiltype groups (HR 7.7, 95% CI 3.6 – 14.2; log-rank for trend p = 2e−9). (B) The median OS of patients with EGFR/RB1/TP53-altered lung cancer was 29.1 months as compared to 40.8 months in EGFR/TP53-mutant RB1-wildtype and 56.4 months in patients with EGFR-mutant RB1/TP53-wildtype (HR 1.0 95% CI 0.4 – 2.4, HR 1.8 95% CI 0.7 – 4.3, respectively; log-rank for trend p = 0.16).