Figure 2. Transcription-coupled DSB Repair pathway (TC-DSBR) repairs DSBs occurring in transcriptionally active loci.
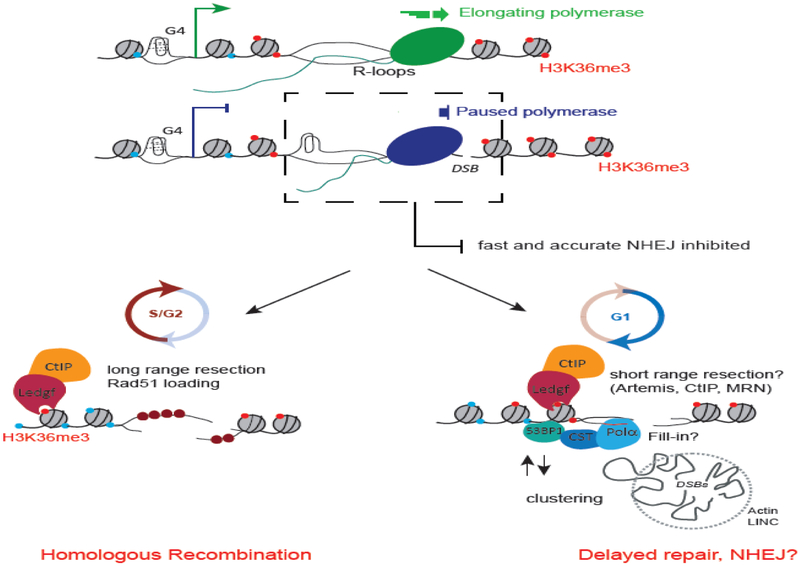
R-loops and G4 structures accumulate at transcribed genes, mainly over TSS and promoter regions, where they can induce DSBs, resulting in a rapid transcriptional arrest of the local elongating RNA polymerases (RNA Pol II) (see Fig. 1). We propose that secondary DNA structures may inhibit fast and accurate NHEJ pathway, consequently triggering DNA ends processing, further stimulated by CtIP recruitment through LEDGF/H3K36me3 interaction. In G1 cells, this short range resection may delay repair and promote DSB clustering [117]. These processed DNA ends may require DNA Polα dependent fill-in to complete repair by NHEJ. In S/G2 cells, long range resection of the 5’ strand allows formation of a 3’ nucleoprotein filament further available for HR repair using the available sister chromatid as a template.
