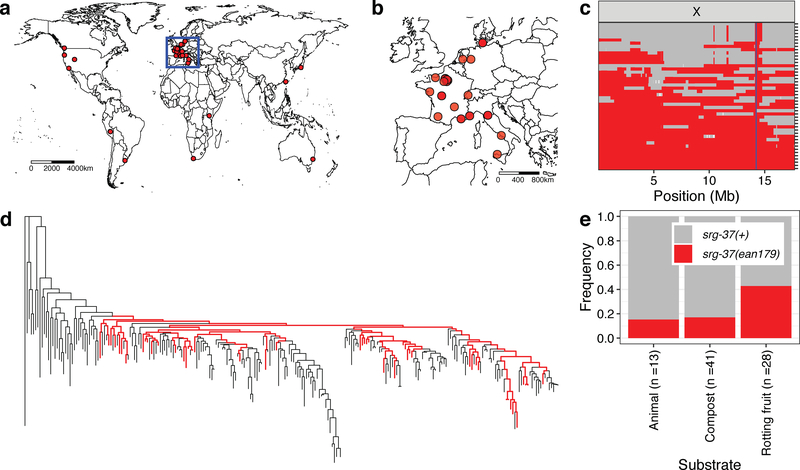
Fig. 4: Worldwide and niche-associated gene flow shape the ascaroside (ascr#5) pheromone receptor locus.
(a) The global distribution of wild strains that contain the srg-37(ean179) deletion allele (red circle) is shown. (b) The geographic distribution of wild strains that are sampled from Europe (inset). Wild strains that contain the srg-37 deletion (red circle) are shown. (a, b) Scale bars are shown in the map. (c) Sharing of the swept haplotype on the X chromosome among 46 wild isotypes with srg-37(ean179) is shown. Each row is one of the 46 isotypes, ordered roughly by the extent of swept-haplotype sharing (red). Other haplotypes are colored grey. Genomic position of X chromosome is shown on the x-axis. The blue line shows the position of the srg-37 locus. (d) The genome-wide tree of 249 C. elegans wild isolates with those strains that have the srg-37 deletion shown as red. (e) Stacked bar plots of srg-37(+) (grey) and srg-37(ean179) (red) allele frequencies among three subpopulations that were sampled from different substrates across hybrid zone in Europe (see Materials and methods). Substrate types and sample sizes are shown on the x-axis, and allele frequencies of each allele are shown on the y-axis.