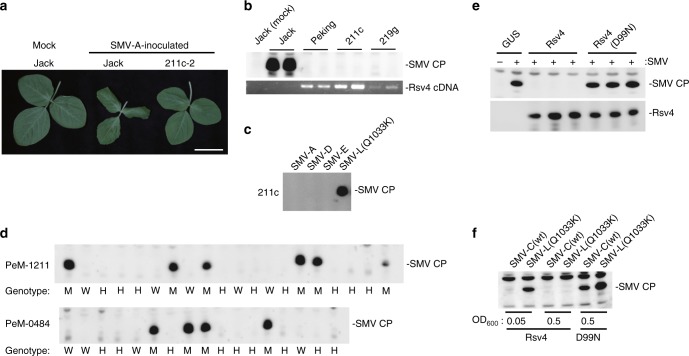
Fig. 2.
Rsv4 encodes an RNase H family protein. a Symptoms of SMV-inoculated soybean plants. 211c-2 is a transgenic line derived from susceptible cv. Jack, overexpressing Rsv4 from Peking. Bar = 5 cm. b SMV coat protein (CP) accumulation in control and transgenic soybean plants. 211c expresses Rsv4 cDNA driven by the cauliflower mosaic virus 35 S promoter, while 219 g carries a genomic DNA fragment of Peking containing the putative native promoter of Rsv4. SMV CP accumulation in non-inoculated upper leaves was detected by western blotting at 10 days post-inoculation (dpi) (upper panel). Rsv4 mRNA was detected by RT-PCR (lower panel). Lanes represent individual plants. c SMV strains SMV-A, -D, -E, and -L(Q1033K) were used to inoculate 211c, and CP accumulation was analyzed as in panel b. d Co-segregation of PeM-1211 and PeM-0484 (identical nonsense mutations in Peking Rsv4 gene) and SMV-susceptible phenotype. W wild-type, M mutant-type, H heterozygous. e Rsv4, but not the Rsv4(D99N) mutant protein, inhibits SMV multiplication in N. benthamiana leaves. SMV CP accumulation was detected by western blotting at 5 dpi. f SMV-L(Q1033K) is less sensitive to Rsv4 than SMV-C. Agrobacterium strains containing constructs to express Rsv4 or Rsv4(D99N) were infiltrated at the indicated concentrations. 1 day after infiltration, Agrobacterium harboring SMV cDNA was infiltrated at OD600 = 0.005. CP accumulation was detected at 7 dpi. The source data of Fig. 2b-f are provided as a Source Data file