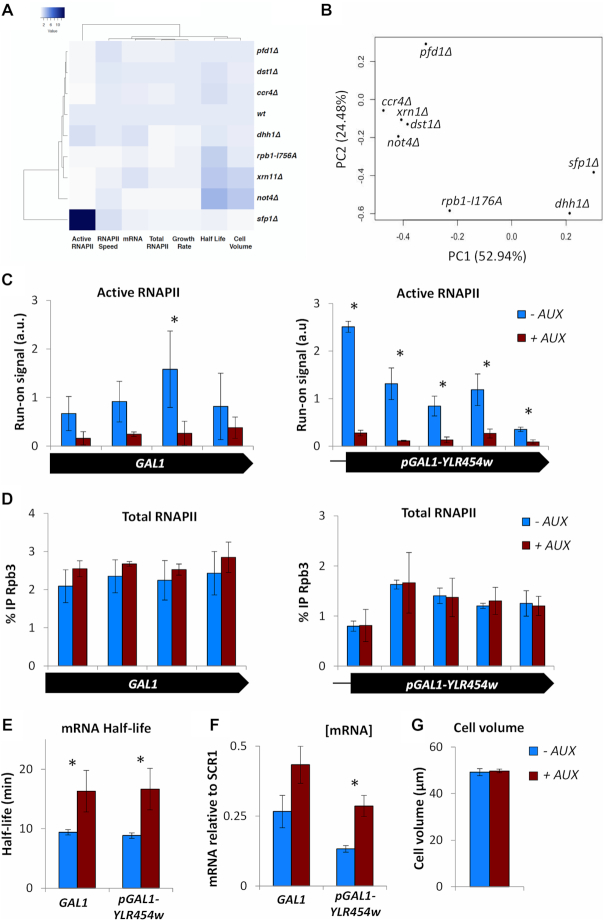
Figure 4.
Lack of Xrn1 phenotypically associates with lack of TFIIS and provokes fast inactivation of elongating RNAPII. (A) Spearman hierarchical clustering of all the data summarized in Supplementary Figure S2B. xrn1Δ primarily associates with rpb1-I746A. (B) A principal component analysis of the same data associates mRNA decay mutants with dst1Δ. The first component (PC1) explains 52.94% of the variables and the second component (PC2) the 24.48%. (C) Active RNAPII along the GAL1 and GAL1p-YLR454w gene is decreased in an Xrn1-AID strain, where Xrn1 is rapidly depleted from the cell upon the addition of auxin. Here, we compare the control (-AUX) to Xrn1-depleted cells (+AUX). (D) Total RNAPII is unaffected along the GAL1 and GAL1p-YLR454w genes when comparing control to Xrn1 depleted cells. (E) The mRNA half-life of GAL1 and GAL1p-YLR454w is significantly increased upon Xrn1 depletion. (F) Apparent [mRNA] of both genes is also increased upon Xrn1 depletion. (G) Cell volume is unaffected after depleting Xrn1 for 1 h. All bars represent mean and standard deviation of three biological replicates (* if p< 0.05 in a Student’s t-test).