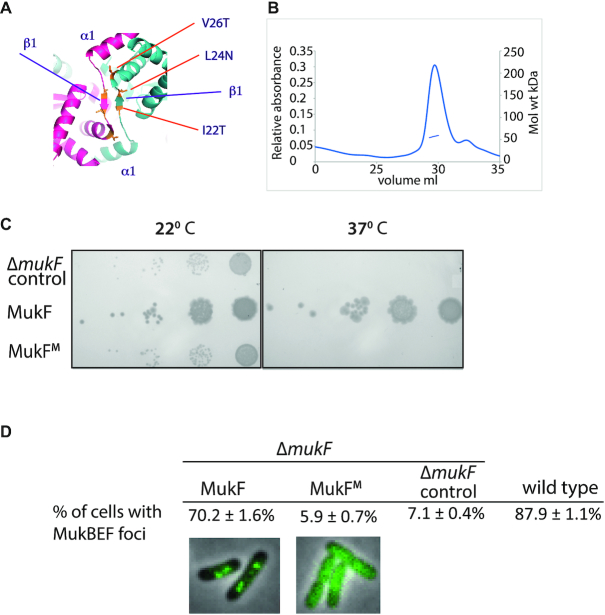
Figure 6.
Escherichia coli cells expressing monomeric MukF have a Muk− phenotype and fail to form MukBEF clusters on the chromosome. (A) Dimerisation interface of MukF showing the three mutated residues, I22T, L24N, V26T. (B) SEC-MALS of MukF monomers. The observed mass of 57.3 kDa corresponded to theoretical mass, of 52.9 kDa, of the monomeric variant. A small shoulder in the elution profile reflects the presence of the protein proteolytic cleavage product. (C) Temperature-sensitivity of growth in rich medium assay. 102-fold serial dilutions of ΔmukF cells containing plasmid pET21 expressing basal levels of wild-type MukF or the MukF monomer (MukFM) are shown, alongside a control in which cells contain the plasmid vector alone. (D) ΔmukF cells expressing MukF monomers (MukFM) fail to form MukBEF foci. The analysis of foci formation was performed in ΔmukF strain carrying C-terminal mukB-gfp fusion; MukF and MukFM were expressed from pET21 as in (C). For comparison, foci formation in a strain carrying the intact endogenous chromosomal copy of mukF was monitored using MukB-mYpet expression (SN192), (15).