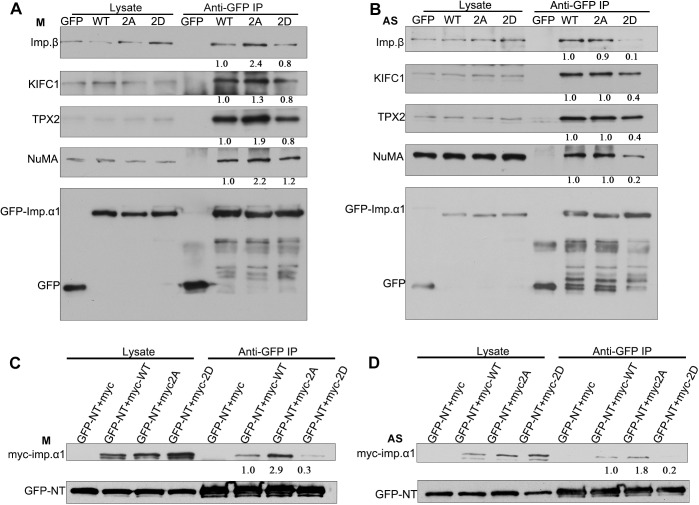
Fig. 4.
Phosphorylation at T9 and S62 attenuates the interaction of importin-α1 with importin-β and NLS-containing SAFs in mitosis. (A) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with GFP, GFP–importin-α1 WT, GFP-importin-α1 2A or GFP–importin-α1 2D and were arrested in mitosis (labeled M) with 100 ng/ml of nocodazole for 17 h. GFP–importin-α1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from mitotic cells using anti-GFP antibody, followed by immunoblotting for importin-β, KIFC1, TPX2, NuMA and GFP. Cell lysates used for the precipitations are shown in the left panels. (B) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with either GFP, GFP–importin-α1 WT, GFP–importin-α1 2A or GFP–importin-α1 2D and were collected as asynchronous (labeled AS) cells. GFP–importin-α1 was immunoprecipitated from asynchronous cells using the anti-GFP antibody, followed by immunoblotting for importin-β, KIFC1, TPX2, NuMA and GFP. Cell lysates used for the precipitations are shown in the left panels. (C) T9 and S62 phosphorylation may function in an NLS-dependent manner in mitosis. HeLa cells were co-transfected with the NLS-containing fragment GFP–NT and Myc-tagged importin-α1 or mutants [Myc-importin-α1 WT (myc-WT), the non-phosphorylation-mimicking double-mutant Myc-importin-α1 2A (myc-2A) and phosphorylation-mimicking double-mutant Myc-importin-α1 2D (myc-2D)] and then were arrested in mitosis with 100 ng/ml of nocodazole for 17 h. GFP–NT was immunoprecipitated from mitotic cells using an anti-GFP antibody, followed by immunoblotting for Myc and GFP. (D) HeLa cells were co-transfected with the NLS-containing fragment GFP–NT and Myc-tagged importin-α1 or mutants as in C, and then were collected as asynchronous cells. GFP–NT was immunoprecipitated from asynchronous cells using an anti-GFP antibody, followed by immunoblotting for Myc and GFP. The numbers under the bands refer to the relative grey value intensity.