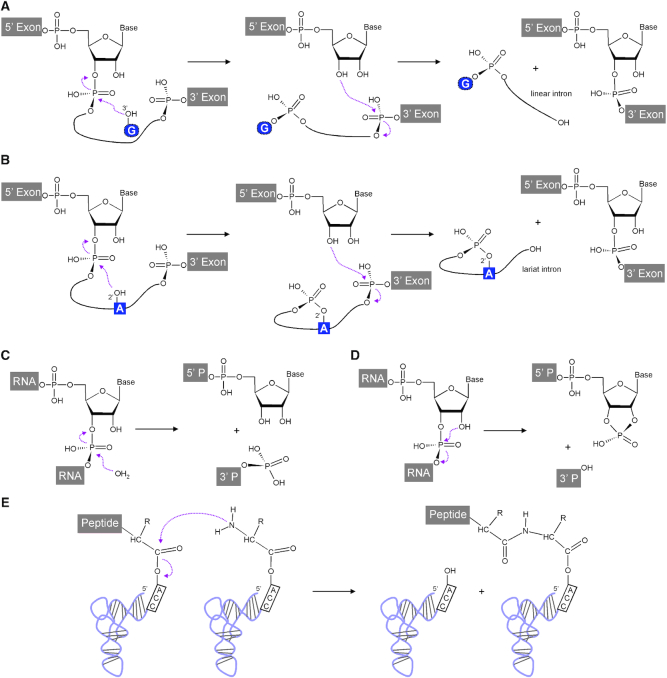
Figure 1.
Reactions naturally catalysed by RNA. Two sequential transesterification reactions catalysed by group I. (A) and group II (B) introns in cis. These result in joined exons and linear and lariat introns, respectively. RNA hydrolysis catalysed in trans by the M1 RNA subunit of bacterial RNase P. (C) results in a phosphate containing 5′ end of the mature tRNA as the 3′ cleavage product (3′ P) and a 3′ hydroxyl group at the 5′ cleavage product (5′ P). Small nucleolytic ribozymes undergo transesterification reactions in cis (D), in which a specific 2′-hydroxyl attacks the neighbouring 3′,5′-phosphodiester bond. This results in a 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate and a 5′ hydroxyl at the 5′ and 3′ cleavage products, respectively. (E) Peptide bond formation catalysed in the ribosomal peptidyl transferase centre. This figure was adapted from (163).