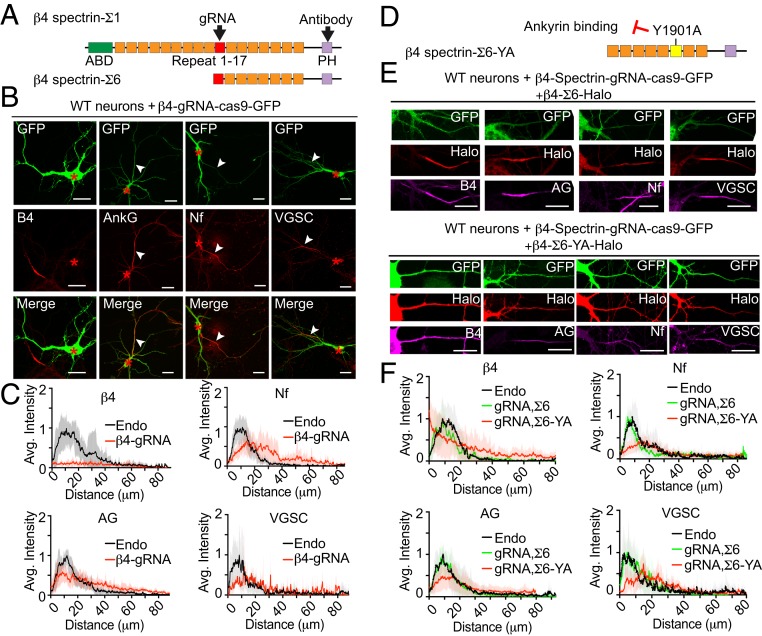
Fig. 3.
Knockout of β4-spectrin phenocopies human neurodevelopmental ANK3 mutations. (A) Schematic of β4-spectrin-Σ1 and Σ6 polypeptides. Actin-binding domain (ABD), pleckstrin homology domain (PH), and the 17 spectrin repeats (SRs) are indicated. The target sites of gRNA and the spectrin antibody are indicated with black arrowheads. (B) Wild-type hippocampal neurons were transfected on 3 DIV with a single construct containing CRISPR-Cas9 cDNA fused with GFP and a gRNA targeting β4-spectrin. Neurons were fixed at 7 DIV and stained with indicated antibodies. Red asterisks indicate the cell body of transfected neurons and white arrowheads indicate the position of AISs (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (C) Average intensity of indicated antibody staining at the AIS is plotted and aligned for β4-spectrin gRNA transfected neurons (red line) and nontransfected neurons (endo, black line) on the same coverslip. n = 10. Results were repeated in 3 independent cultures using gRNA targeting 4 different regions. (D) Schematic of β4-spectrin-Σ6 labeled with Y1901A mutation site, which eliminated the interaction with ankyrin. The AnkG-binding region in SR 15 is highlighted in yellow. (E) The 3 DIV wild-type hippocampal neurons were cotransfected with β4-spectrin-gRNA and β4-spectrin-Σ6-Halo or Σ6-YA-Halo. On 7 DIV, neurons were incubated with JF549 halo dye followed by staining with indicated antibody (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (F) Average intensity of indicated antibody along the AIS is plotted for transfected neurons (β4-spectrin-Σ6 rescue in green line and YA mutant rescue in red line) and aligned with nontransfected neurons (endo, black line). n = 10 of each plot. Results were repeated in 3 independent experiments.