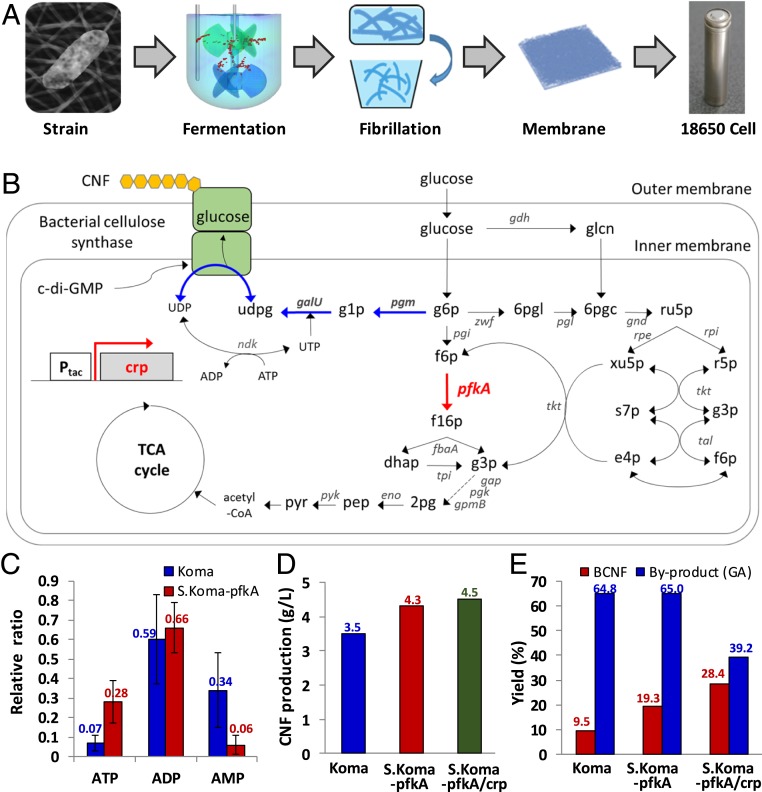
Fig. 1.
Overall process for cellulose nanofiber (CNF) production and battery manufacture, and the metabolic engineering of a CNF-producing strain. (A) Overall scheme for the construction of a bacterial CNF membrane for battery separators. (B) Schematic representation of the CNF production pathway in a metabolically engineered strain (S.Koma-pfkA/crp). The blue lines represent the CNF biosynthesis pathway from glucose 6-phosphate. The bold red arrows indicate the heterologous expression of pfkA and crp gene under the control of the tac promoter. Details for the construction of plasmids, abbreviations of genes and metabolites, and the primers used for gene modification are available in SI Appendix, Tables S1 and S2. (C) Intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), and adenosine monophosphate (AMP) ratio in wild-type Koma and S.Koma-pfkA strains. The error bar represents the SD of 3 measurements. (D) CNF production and (E) yield of Koma, S.Koma-pfkA, and S.Koma-pfkA/crp, respectively. The yield of the by-product, gluconic acid (GA), is also shown in E.