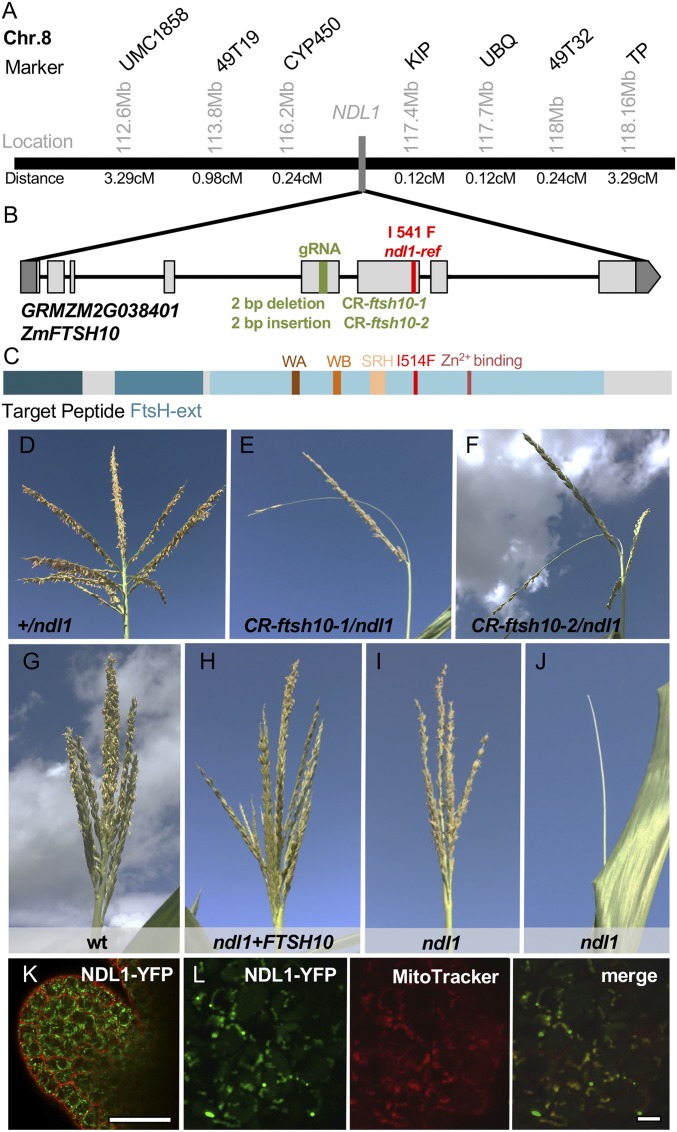
Fig. 2.
NDL1 encodes ZmFTSH10. (A) Positional cloning of NDL1. Molecular markers used and physical (Mb) and genetic distances (cM) are indicated. (B) Schematic representation of the ZmFTSH10 gene and the position of the mutant alleles. Exons and UTRs are depicted as light gray and dark gray rectangles, respectively. The green bar indicates the guide RNA targeting site. The red bar positions the missense mutation. (C) Schematic representation of the ZmFTSH10 protein. FtsH-ext, FtsH-extracellular domain (Pfam); SRH, Second Region of Homology motif; WA, Walker A motif; WB, Walker B motif. (D–F) The tassel phenotype of wild type and ndl1 mutants generated by CRISPR-Cas9. (G–J) The variable tassel phenotype of ndl1 (I and J) is rescued by the pZmFTSH10::FTSH10-YFP construct. (K) Confocal images of an ear AM expressing FTSH10-YFP, counterstained with propidium iodide. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (L) Confocal images of immature ear AMs expressing NDL1-YFP stained with MitoTracker Red CMXRos. (Scale bars, 10 μm.)