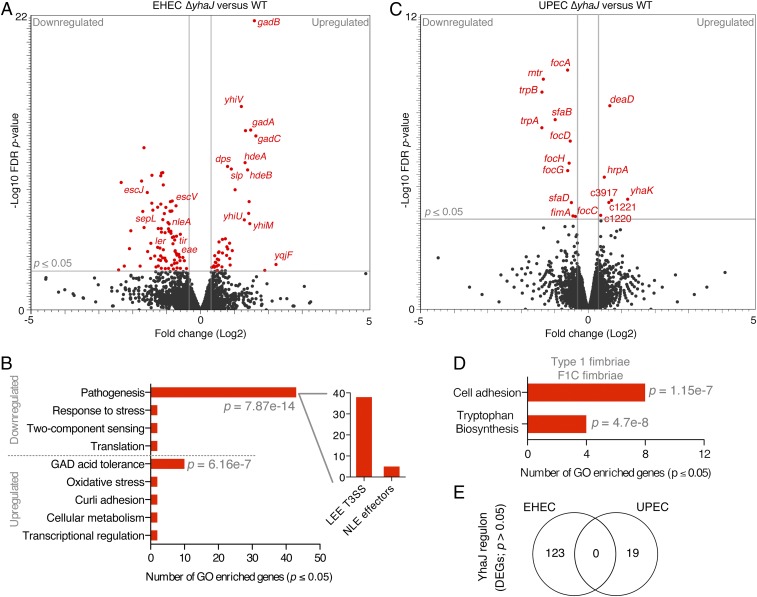
Fig. 1.
YhaJ regulon is unique in 2 distinct E. coli pathotypes. (A) Volcano plot of RNA-seq transcriptome data displaying the pattern of gene expression values for ΔyhaJ relative to WT EHEC cultured in MEM-Hepes (data analyzed from ref. 20). Significantly differentially expressed genes (FDR-corrected P ≤ 0.05) are highlighted in red, with the gray lines representing the boundary for identification of up- or down-regulated genes. Selected genes related to the T3SS, acid tolerance, and known YhaJ targets are indicated. (B) Gene ontology analysis of EHEC DEGs identifying significantly enriched functional categories (P ≤ 0.05). The major groups are highlighted, and the Inset graph depicts the number of genes related to the LEE island or non–LEE-encoded effectors. (C) Volcano plot of RNA-seq transcriptome data displaying the pattern of gene expression values for ΔyhaJ versus WT UPEC cultured identically as EHEC. (D) Gene ontology analysis of UPEC DEGs with the class of adhesion genes highlighted above. (E) Venn diagram comparing the YhaJ regulon of EHEC and UPEC illustrating the lack of any commonality in significant DEGs. All transcriptome experiments were performed in biological triplicate.