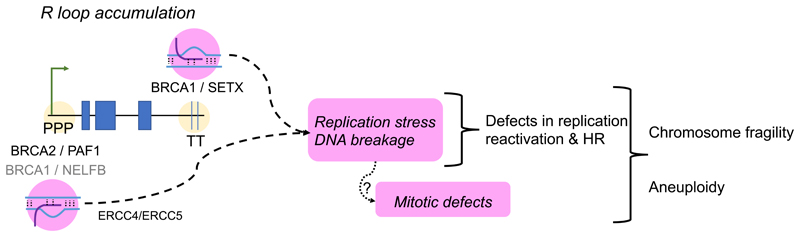
Figure 2. R-loop accumulation and chromosome instability in BRCA-deficient cells.
The schematic depicts how transcription-associated R loop accumulation in BRCA2-deficient cells may be a major source of replication stress and DNA damage leading to chromosome fragility. Roles are shown for BRCA1 and BRCA2 in R-loop turnover at the promoter-proximal pausing (PPP) sites, or at transcription termination (TT) sequences, of expressed genes. The RNAPII regulatory factors PAF1 and NELFB work with BRCA2 and BRCA1 respectively, in the switch from pausing to elongation. Senataxin (SETX) is recruited by BRCA1 to TT sites. The ERCC4/ERCC5 nuclease has been implicated in R-loop cleavage to form DNA breaks.