Figure 5.
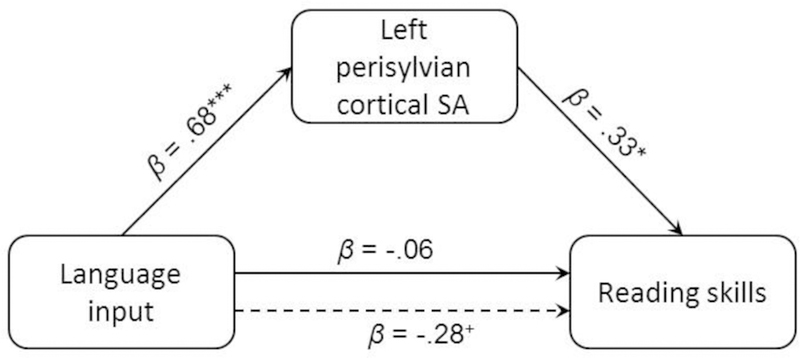
Home language input was significantly indirectly associated with children’s reading skills via left perisylvian cortical surface area (SA; N = 42). The solid line from language input to reading skills represents the total association (c path). The dotted line represents the direct association (c’ path). Covariates were child age, sex, ethnicity, audio recording time, and parental education. + p < .10; * p < .05; *** p < .001
