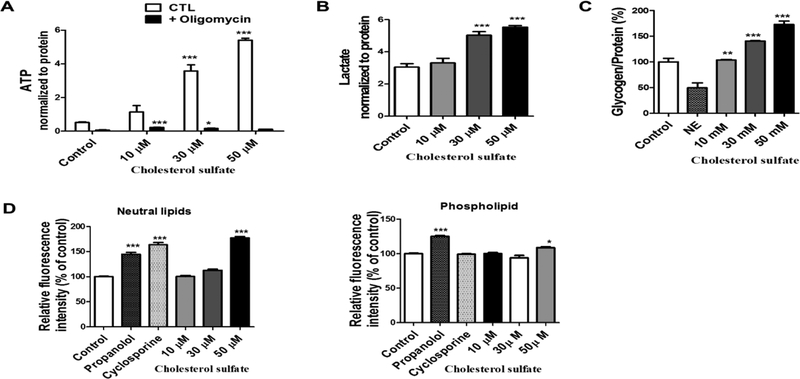
Figure 7. CS enhanced ATP production and increased glycogen content in astrocyte.
(A) Total ATP content in primary astrocytes analyzed using an ATP kit were increased in astrocytes treated with CS (F3,23 = 61.13, p < 0.0001 N=4) and oligomycin introduction (F1,23 = 307.83, p < 0.0001 N=4) as well as a significant oligomycin and treatment(CS) interaction (F3,23 = 62.15, p < 0.0001 N=4). (Two way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s test), significance at * p< 0.05, ** p< 0.01, ***p<0.001 vs control. (B) Lactate levels were increased in primary astrocytes treated with CS (F3,28 = 31.83, p < 0.0001 N=8). (C) Glycogen content was increased in primary astrocytes treated with CS but not norepinephrine (NE) (decreases glycogen storage) (F4,15 = 56.46, p < 0.0001 N=4). (D) Quantitative analysis of lipid content in astrocytes treated with CS, propranolol (induces accumulation of phospholipids) and (cyclosporine induces formation of prominent neutral lipid droplets) shows an increase in neutral lipids (F5,42 = 131.0, p < 0.0001 N=8) and phospholipids (F5,42 = 37.37, p < 0.0001 N=8). in astrocytes treated with propranolol, cyclosporine and 50 μM CS. (One way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s test), significance at * p< 0.05, ** p< 0.01, ***p<0.001 vs control.